Star in the constellation of Octans
CW Octantis
Observation dataEpoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS )
Constellation
Octans
Right ascension 17h 00m 58.51777s [ 2]
Declination
−86° 21′ 51.4707″[ 2]
Apparent magnitude (V)6.03± 0.01[ 3]
Characteristics
Evolutionary stage
subgiant [ 4]
Spectral type
A3 IV[ 5]
U−B color index
+0.02[ 6]
B−V color index
+0.05[ 6]
Variable type
α2 CVn [ 7]
Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv )7.1± 0.5[ 8] km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: +8.413 mas /yr [ 2] Dec.: −0.032 mas /yr [ 2] Parallax (π)5.1828± 0.0486 mas [ 2] Distance 629 ± 6 ly pc ) Absolute magnitude (MV )−0.36[ 9] Details Mass 2.98± 0.05[ 4] M ☉ Radius 4.64[ 10] R ☉ Luminosity 111[ 11] L ☉ Surface gravity (log g )3.45± 0.07[ 12] cgs Temperature 8,791[ 13] K Metallicity [Fe/H] +0.6[ 14] dex Rotation ≈2.8 days [ 13] Rotational velocity (v sin i )92± 6[ 13] Age 188± 4[ 4] Myr Other designations 26 G. Octantis [ 15] CW Octantis , CD −86°100CPD −86°333FK5 921GC 22519HD 148542HIP 83255HR 6139SAO 258751[ 16] Database references SIMBAD data
CW Octantis , also known as HD 148542 , is a solitary, white hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans . It has an apparent magnitude of 6.03, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye . Parallax measurements from Gaia DR3 place the object at a distance of 629 light years . It appears to be receding from the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of km/s
CW Octantis has a stellar classification of A3 IV, indicating that it is an evolved A-type star heading towards the red giant branch . Zorec and Royer (2012) model it as a dwarf star that has just reached the end of its main sequence lifetime.[ 4] mass of the Sun [ 4] radius .[ 10] luminosity of the Sun [ 11] photosphere at an effective temperature of K [ 13] million years old.[ 4]
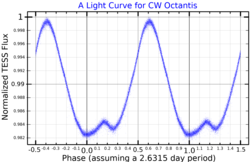
This object is classified as a Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable .[ 7] spectra , but CW Octantis seems to be ordinary. Renson and Manfroid (2009) consider its peculiarity status to be doubtful.[ 17] Hipparcos passband within 2.63 days .[ 18] projected rotational velocity of km/s [ 13]
References
^ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes" . Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 1 October 2022 .^ a b c d Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties" . Astronomy and Astrophysics . 674 : A1. arXiv :2208.00211 Bibcode :2023A&A...674A...1G . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 S2CID 244398875 . Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR .^ Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (March 2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 355 : L27 – L30 . Bibcode :2000A&A...355L..27H . ISSN 0004-6361 . ^ a b c d e f Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (January 2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities" . Astronomy and Astrophysics . 537 : A120. arXiv :1201.2052 Bibcode :2012A&A...537A.120Z . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/201117691 ISSN 0004-6361 . S2CID 55586789 . ^ de Vaucouleurs, A. (1 August 1957). "Spectral Types and Luminosities of B, A and F Southern Stars" . Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society . 117 (4): 449– 462. Bibcode :1957MNRAS.117..449D . doi :10.1093/mnras/117.4.449 eISSN 1365-2966 . ISSN 0035-8711 . ^ a b Johnson, H. L.; Mitchell, R. I.; Iriarte, B.; Wisniewski, W. Z. (1966). "UBVRIJKL Photometry of the Bright Stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory . 4 : 99– 110. Bibcode :1966CoLPL...4...99J . ^ a b Samus’, N. N.; Goranskii, V. P.; Durlevich, O. V.; Zharova, A. V.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N.; Williams, D. B.; Hazen, M. L. (July 2003). "An electronic version of the second volume of the General Catalogue of Variable Stars with improved coordinates". Astronomy Letters . 29 (7): 468– 479. Bibcode :2003AstL...29..468S . doi :10.1134/1.1589864 . eISSN 1562-6873 . ISSN 1063-7737 . S2CID 16299532 . ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35,495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters . 32 (11): 759– 771. arXiv :1606.08053 Bibcode :2006AstL...32..759G . doi :10.1134/S1063773706110065 . eISSN 1562-6873 . ISSN 1063-7737 . S2CID 119231169 . ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (May 2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters . 38 (5): 331– 346. arXiv :1108.4971 Bibcode :2012AstL...38..331A . doi :10.1134/S1063773712050015 . eISSN 1562-6873 . ISSN 1063-7737 . S2CID 119257644 . ^ a b Kervella, Pierre; Arenou, Frédéric; Thévenin, Frédéric (2022). "Stellar and substellar companions from Gaia EDR3" . Astronomy & Astrophysics . 657 : A7. arXiv :2109.10912 Bibcode :2022A&A...657A...7K . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/202142146 eISSN 1432-0746 . ISSN 0004-6361 . ^ a b McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (21 November 2012). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars: Parameters and IR excesses from Hipparcos" . Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society . 427 (1): 343– 357. arXiv :1208.2037 Bibcode :2012MNRAS.427..343M . doi :10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x ISSN 0035-8711 . ^ Stassun, Keivan G.; et al. (9 September 2019). "The Revised TESS Input Catalog and Candidate Target List" . The Astronomical Journal . 158 (4): 138. arXiv :1905.10694 Bibcode :2019AJ....158..138S . doi :10.3847/1538-3881/ab3467 eISSN 1538-3881 . ^ a b c d e Reiners, A.; Royer, F. (February 2004). "First signatures of strong differential rotation in A-type stars" . Astronomy & Astrophysics . 415 (1): 325– 329. arXiv :astro-ph/0311341 Bibcode :2004A&A...415..325R . doi :10.1051/0004-6361:20034175 eISSN 1432-0746 . ISSN 0004-6361 . ^ Rainer, M.; Poretti, E.; Mistò, A.; Panzera, M. R.; Molinaro, M.; Cepparo, F.; Roth, M.; Michel, E.; Monteiro, M. J. P. F. G. (5 December 2016). "The SpaceInn-SISMA Database: Characterization of a Large Sample of Variable and Active Stars by Means of Harps Spectra" . The Astronomical Journal . 152 (6): 207. arXiv :1611.02715 Bibcode :2016AJ....152..207R . doi :10.3847/0004-6256/152/6/207 eISSN 1538-3881 . ^ Gould, Benjamin Apthorp (1878). "Uranometria Argentina : brillantez y posicion de las estrellas fijas, hasta la septima magnitud, comprendidas dentro de cien grados del polo austral : con atlas". Resultados del Observatorio Nacional Argentino . 1 . Bibcode :1879RNAO....1.....G . ^ "CW Oct" . SIMBAD Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved October 1, 2022 .^ Renson, P.; Manfroid, J. (19 March 2009). "Catalogue of Ap, HgMn and Am stars" . Astronomy & Astrophysics . 498 (3): 961– 966. Bibcode :2009A&A...498..961R . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/200810788 eISSN 1432-0746 . ISSN 0004-6361 . ^ Watson, C. L.; Henden, A. A.; Price, A. (May 2006). "The International Variable Star Index (VSX)". Society for Astronomical Sciences Annual Symposium . 25 : 47. Bibcode :2006SASS...25...47W .