Multi-chassis link aggregation group
A multi-chassis link aggregation group (MLAG or MC-LAG) is a type of link aggregation group (LAG) with constituent ports that terminate on separate chassis, primarily for the purpose of providing redundancy in the event one of the chassis fails. The IEEE 802.1AX-2008 industry standard for link aggregation does not mention MC-LAG, but does not preclude it. Its implementation varies by vendor; notably, the protocol for coordination between chassis is proprietary. BackgroundA LAG is a method of inverse multiplexing over multiple Ethernet links, thereby increasing bandwidth and providing redundancy. It is defined by the IEEE 802.1AX-2008 standard, which states, "Link Aggregation allows one or more links to be aggregated together to form a Link Aggregation Group, such that a MAC client can treat the Link Aggregation Group as if it were a single link."[1] This layer 2 transparency is achieved by the LAG using a single MAC address for all the device’s ports in the LAG group. LAG can be configured as either static or dynamic. Dynamic LAG uses a peer-to-peer protocol, called Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP), for control. This LACP protocol is also defined within the 802.1AX-2008 standard. Multi-chassisMC-LAG adds node-level redundancy to the normal link-level redundancy that a LAG provides. This allows two or more nodes to share a common LAG endpoint. The multiple nodes present a single logical LAG to the remote end. Note that MC-LAG implementations are vendor-specific, but cooperating chassis remain externally compliant to the IEEE 802.1AX-2008 standard.[2] Nodes in an MC-LAG cluster communicate to synchronize and negotiate automatic switchovers in the event of failure. Some implementations may support administrator-initiated switchovers. The diagram here shows four configurations: 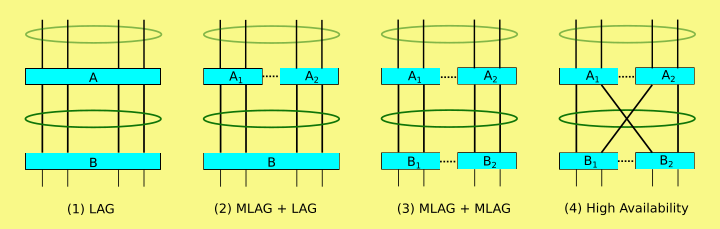
ImplementationsThe following table lists known vendor implementations of MC-LAG, all of which are proprietary.
AlternativesThe link aggregation configuration is superior to Spanning Tree Protocol as the load can be shared across all links during normal operation, whereas Spanning Tree Protocol must disable some links to prevent loops. With Spanning Tree Protocol there is a potential delay when recovering from failure. Link aggregation typically can recover quickly from failure. IEEE 802.1aq (Shortest Path Bridging) is an alternative to MC-LAG that can be used for complex networks.[6] TRILL (TRansparent Interconnection of Lots of Links) allows Ethernet to use an arbitrary topology, and enables per-flow pair-wise load splitting by way of Dijkstra's algorithm without configuration or user intervention. References
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia













