Square root of 3
The square root of 3 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number 3. It is denoted mathematically as or . It is more precisely called the principal square root of 3 to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. The square root of 3 is an irrational number. It is also known as Theodorus' constant, after Theodorus of Cyrene, who proved its irrationality.[1] In 2013, its numerical value in decimal notation was computed to ten billion digits.[2] Its decimal expansion, written here to 65 decimal places, is given by OEIS: A002194:
Archimedes reported a range for its value: .[3] The upper limit is an accurate approximation for to (six decimal places, relative error ) and the lower limit to (four decimal places, relative error ). Geometry and trigonometryThe height of an equilateral triangle with edge length 2 is √3. Also, the long leg of a 30-60-90 triangle with hypotenuse 2. And, the height of a regular hexagon with sides of length 1 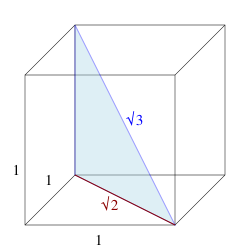 The square root of 3 can be found as the leg length of an equilateral triangle that encompasses a circle with a diameter of 1. If an equilateral triangle with sides of length 1 is cut into two equal halves, by bisecting an internal angle across to make a right angle with one side, the right angle triangle's hypotenuse is length one, and the sides are of length and . From this, , , and . The square root of 3 also appears in algebraic expressions for various other trigonometric constants, including[4] the sines of other angles. It is the distance between parallel sides of a regular hexagon with sides of length 1. It is the length of the space diagonal of a unit cube. The vesica piscis has a major axis to minor axis ratio equal to . This can be shown by constructing two equilateral triangles within it. References
Further reading
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Square root of 3.
|
||||||||
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia



































