Test functions for optimization Functions used to evaluate optimization algorithms
In applied mathematics, test functions , known as artificial landscapes , are useful to evaluate characteristics of optimization algorithms, such as convergence rate , precision, robustness and general performance.
Here some test functions are presented with the aim of giving an idea about the different situations that optimization algorithms have to face when coping with these kinds of problems. In the first part, some objective functions for single-objective optimization cases are presented. In the second part, test functions with their respective Pareto fronts for multi-objective optimization problems (MOP) are given.
The artificial landscapes presented herein for single-objective optimization problems are taken from Bäck,[ 1] [ 2] [ 3]
The test functions used to evaluate the algorithms for MOP were taken from Deb,[ 4] [ 5] [ 6] [ 7] [ 8]
Just a general form of the equation, a plot of the objective function, boundaries of the object variables and the coordinates of global minima are given herein.
Test functions for single-objective optimization
Name
Plot
Formula
Global minimum
Search domain
Rastrigin function
f
(
x
)
=
A
n
+
∑
i
=
1
n
[
x
i
2
−
A
cos
(
2
π
x
i
)
]
{\displaystyle f(\mathbf {x} )=An+\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left[x_{i}^{2}-A\cos(2\pi x_{i})\right]}
where:
A
=
10
{\displaystyle {\text{where: }}A=10}
f
(
0
,
…
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,\dots ,0)=0}
−
5.12
≤
x
i
≤
5.12
{\displaystyle -5.12\leq x_{i}\leq 5.12}
Ackley function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
−
20
exp
[
−
0.2
0.5
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
]
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-20\exp \left[-0.2{\sqrt {0.5\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)}}\right]}
−
exp
[
0.5
(
cos
2
π
x
+
cos
2
π
y
)
]
+
e
+
20
{\displaystyle -\exp \left[0.5\left(\cos 2\pi x+\cos 2\pi y\right)\right]+e+20}
f
(
0
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,0)=0}
−
5
≤
x
,
y
≤
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x,y\leq 5}
Sphere function
f
(
x
)
=
∑
i
=
1
n
x
i
2
{\displaystyle f({\boldsymbol {x}})=\sum _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}^{2}}
f
(
x
1
,
…
,
x
n
)
=
f
(
0
,
…
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(x_{1},\dots ,x_{n})=f(0,\dots ,0)=0}
−
∞
≤
x
i
≤
∞
{\displaystyle -\infty \leq x_{i}\leq \infty }
1
≤
i
≤
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
Rosenbrock function
f
(
x
)
=
∑
i
=
1
n
−
1
[
100
(
x
i
+
1
−
x
i
2
)
2
+
(
1
−
x
i
)
2
]
{\displaystyle f({\boldsymbol {x}})=\sum _{i=1}^{n-1}\left[100\left(x_{i+1}-x_{i}^{2}\right)^{2}+\left(1-x_{i}\right)^{2}\right]}
Min
=
{
n
=
2
→
f
(
1
,
1
)
=
0
,
n
=
3
→
f
(
1
,
1
,
1
)
=
0
,
n
>
3
→
f
(
1
,
…
,
1
⏟
n
times
)
=
0
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}n=2&\rightarrow \quad f(1,1)=0,\\n=3&\rightarrow \quad f(1,1,1)=0,\\n>3&\rightarrow \quad f(\underbrace {1,\dots ,1} _{n{\text{ times}}})=0\\\end{cases}}}
−
∞
≤
x
i
≤
∞
{\displaystyle -\infty \leq x_{i}\leq \infty }
1
≤
i
≤
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
Beale function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
1.5
−
x
+
x
y
)
2
+
(
2.25
−
x
+
x
y
2
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\left(1.5-x+xy\right)^{2}+\left(2.25-x+xy^{2}\right)^{2}}
+
(
2.625
−
x
+
x
y
3
)
2
{\displaystyle +\left(2.625-x+xy^{3}\right)^{2}}
f
(
3
,
0.5
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(3,0.5)=0}
−
4.5
≤
x
,
y
≤
4.5
{\displaystyle -4.5\leq x,y\leq 4.5}
Goldstein–Price function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
[
1
+
(
x
+
y
+
1
)
2
(
19
−
14
x
+
3
x
2
−
14
y
+
6
x
y
+
3
y
2
)
]
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\left[1+\left(x+y+1\right)^{2}\left(19-14x+3x^{2}-14y+6xy+3y^{2}\right)\right]}
[
30
+
(
2
x
−
3
y
)
2
(
18
−
32
x
+
12
x
2
+
48
y
−
36
x
y
+
27
y
2
)
]
{\displaystyle \left[30+\left(2x-3y\right)^{2}\left(18-32x+12x^{2}+48y-36xy+27y^{2}\right)\right]}
f
(
0
,
−
1
)
=
3
{\displaystyle f(0,-1)=3}
−
2
≤
x
,
y
≤
2
{\displaystyle -2\leq x,y\leq 2}
Booth function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
+
2
y
−
7
)
2
+
(
2
x
+
y
−
5
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\left(x+2y-7\right)^{2}+\left(2x+y-5\right)^{2}}
f
(
1
,
3
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(1,3)=0}
−
10
≤
x
,
y
≤
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
Bukin function N.6
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
100
|
y
−
0.01
x
2
|
+
0.01
|
x
+
10
|
.
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=100{\sqrt {\left|y-0.01x^{2}\right|}}+0.01\left|x+10\right|.\quad }
f
(
−
10
,
1
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(-10,1)=0}
−
15
≤
x
≤
−
5
{\displaystyle -15\leq x\leq -5}
−
3
≤
y
≤
3
{\displaystyle -3\leq y\leq 3}
Matyas function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.26
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
−
0.48
x
y
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.26\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)-0.48xy}
f
(
0
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,0)=0}
−
10
≤
x
,
y
≤
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
Lévi function N.13
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
sin
2
3
π
x
+
(
x
−
1
)
2
(
1
+
sin
2
3
π
y
)
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin ^{2}3\pi x+\left(x-1\right)^{2}\left(1+\sin ^{2}3\pi y\right)}
+
(
y
−
1
)
2
(
1
+
sin
2
2
π
y
)
{\displaystyle +\left(y-1\right)^{2}\left(1+\sin ^{2}2\pi y\right)}
f
(
1
,
1
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(1,1)=0}
−
10
≤
x
,
y
≤
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
Griewank function
f
(
x
)
=
1
+
1
4000
∑
i
=
1
n
x
i
2
−
∏
i
=
1
n
P
i
(
x
i
)
{\displaystyle f(x)=1+{\frac {1}{4000}}\sum _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}^{2}-\prod _{i=1}^{n}P_{i}(x_{i})}
P
i
(
x
i
)
=
cos
(
x
i
i
)
{\displaystyle P_{i}(x_{i})=\cos \left({\frac {x_{i}}{\sqrt {i}}}\right)}
f
(
0
,
…
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,\dots ,0)=0}
−
∞
≤
x
i
≤
∞
{\displaystyle -\infty \leq x_{i}\leq \infty }
1
≤
i
≤
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
Himmelblau's function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
2
+
y
−
11
)
2
+
(
x
+
y
2
−
7
)
2
.
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=(x^{2}+y-11)^{2}+(x+y^{2}-7)^{2}.\quad }
Min
=
{
f
(
3.0
,
2.0
)
=
0.0
f
(
−
2.805118
,
3.131312
)
=
0.0
f
(
−
3.779310
,
−
3.283186
)
=
0.0
f
(
3.584428
,
−
1.848126
)
=
0.0
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}f\left(3.0,2.0\right)&=0.0\\f\left(-2.805118,3.131312\right)&=0.0\\f\left(-3.779310,-3.283186\right)&=0.0\\f\left(3.584428,-1.848126\right)&=0.0\\\end{cases}}}
−
5
≤
x
,
y
≤
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x,y\leq 5}
Three-hump camel function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
2
x
2
−
1.05
x
4
+
x
6
6
+
x
y
+
y
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=2x^{2}-1.05x^{4}+{\frac {x^{6}}{6}}+xy+y^{2}}
f
(
0
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,0)=0}
−
5
≤
x
,
y
≤
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x,y\leq 5}
Easom function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
−
cos
(
x
)
cos
(
y
)
exp
(
−
(
(
x
−
π
)
2
+
(
y
−
π
)
2
)
)
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-\cos \left(x\right)\cos \left(y\right)\exp \left(-\left(\left(x-\pi \right)^{2}+\left(y-\pi \right)^{2}\right)\right)}
f
(
π
,
π
)
=
−
1
{\displaystyle f(\pi ,\pi )=-1}
−
100
≤
x
,
y
≤
100
{\displaystyle -100\leq x,y\leq 100}
Cross-in-tray function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
−
0.0001
[
|
sin
x
sin
y
exp
(
|
100
−
x
2
+
y
2
π
|
)
|
+
1
]
0.1
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-0.0001\left[\left|\sin x\sin y\exp \left(\left|100-{\frac {\sqrt {x^{2}+y^{2}}}{\pi }}\right|\right)\right|+1\right]^{0.1}}
Min
=
{
f
(
1.34941
,
−
1.34941
)
=
−
2.06261
f
(
1.34941
,
1.34941
)
=
−
2.06261
f
(
−
1.34941
,
1.34941
)
=
−
2.06261
f
(
−
1.34941
,
−
1.34941
)
=
−
2.06261
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}f\left(1.34941,-1.34941\right)&=-2.06261\\f\left(1.34941,1.34941\right)&=-2.06261\\f\left(-1.34941,1.34941\right)&=-2.06261\\f\left(-1.34941,-1.34941\right)&=-2.06261\\\end{cases}}}
−
10
≤
x
,
y
≤
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
Eggholder function [ 9] [ 10]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
−
(
y
+
47
)
sin
|
x
2
+
(
y
+
47
)
|
−
x
sin
|
x
−
(
y
+
47
)
|
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-\left(y+47\right)\sin {\sqrt {\left|{\frac {x}{2}}+\left(y+47\right)\right|}}-x\sin {\sqrt {\left|x-\left(y+47\right)\right|}}}
f
(
512
,
404.2319
)
=
−
959.6407
{\displaystyle f(512,404.2319)=-959.6407}
−
512
≤
x
,
y
≤
512
{\displaystyle -512\leq x,y\leq 512}
Hölder table function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
−
|
sin
x
cos
y
exp
(
|
1
−
x
2
+
y
2
π
|
)
|
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-\left|\sin x\cos y\exp \left(\left|1-{\frac {\sqrt {x^{2}+y^{2}}}{\pi }}\right|\right)\right|}
Min
=
{
f
(
8.05502
,
9.66459
)
=
−
19.2085
f
(
−
8.05502
,
9.66459
)
=
−
19.2085
f
(
8.05502
,
−
9.66459
)
=
−
19.2085
f
(
−
8.05502
,
−
9.66459
)
=
−
19.2085
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}f\left(8.05502,9.66459\right)&=-19.2085\\f\left(-8.05502,9.66459\right)&=-19.2085\\f\left(8.05502,-9.66459\right)&=-19.2085\\f\left(-8.05502,-9.66459\right)&=-19.2085\end{cases}}}
−
10
≤
x
,
y
≤
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
McCormick function
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
sin
(
x
+
y
)
+
(
x
−
y
)
2
−
1.5
x
+
2.5
y
+
1
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin \left(x+y\right)+\left(x-y\right)^{2}-1.5x+2.5y+1}
f
(
−
0.54719
,
−
1.54719
)
=
−
1.9133
{\displaystyle f(-0.54719,-1.54719)=-1.9133}
−
1.5
≤
x
≤
4
{\displaystyle -1.5\leq x\leq 4}
−
3
≤
y
≤
4
{\displaystyle -3\leq y\leq 4}
Schaffer function N. 2
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.5
+
sin
2
(
x
2
−
y
2
)
−
0.5
[
1
+
0.001
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
]
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.5+{\frac {\sin ^{2}\left(x^{2}-y^{2}\right)-0.5}{\left[1+0.001\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right]^{2}}}}
f
(
0
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,0)=0}
−
100
≤
x
,
y
≤
100
{\displaystyle -100\leq x,y\leq 100}
Schaffer function N. 4
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.5
+
cos
2
[
sin
(
|
x
2
−
y
2
|
)
]
−
0.5
[
1
+
0.001
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
]
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.5+{\frac {\cos ^{2}\left[\sin \left(\left|x^{2}-y^{2}\right|\right)\right]-0.5}{\left[1+0.001\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right]^{2}}}}
Min
=
{
f
(
0
,
1.25313
)
=
0.292579
f
(
0
,
−
1.25313
)
=
0.292579
f
(
1.25313
,
0
)
=
0.292579
f
(
−
1.25313
,
0
)
=
0.292579
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}f\left(0,1.25313\right)&=0.292579\\f\left(0,-1.25313\right)&=0.292579\\f\left(1.25313,0\right)&=0.292579\\f\left(-1.25313,0\right)&=0.292579\end{cases}}}
−
100
≤
x
,
y
≤
100
{\displaystyle -100\leq x,y\leq 100}
Styblinski–Tang function
f
(
x
)
=
∑
i
=
1
n
x
i
4
−
16
x
i
2
+
5
x
i
2
{\displaystyle f({\boldsymbol {x}})={\frac {\sum _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}^{4}-16x_{i}^{2}+5x_{i}}{2}}}
−
39.16617
n
<
f
(
−
2.903534
,
…
,
−
2.903534
⏟
n
times
)
<
−
39.16616
n
{\displaystyle -39.16617n<f(\underbrace {-2.903534,\ldots ,-2.903534} _{n{\text{ times}}})<-39.16616n}
−
5
≤
x
i
≤
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x_{i}\leq 5}
1
≤
i
≤
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
Shekel function
f
(
x
→
)
=
∑
i
=
1
m
(
c
i
+
∑
j
=
1
n
(
x
j
−
a
j
i
)
2
)
−
1
{\displaystyle f({\vec {x}})=\sum _{i=1}^{m}\;\left(c_{i}+\sum \limits _{j=1}^{n}(x_{j}-a_{ji})^{2}\right)^{-1}}
or, similarly,
f
(
x
1
,
x
2
,
.
.
.
,
x
n
−
1
,
x
n
)
=
∑
i
=
1
m
(
c
i
+
∑
j
=
1
n
(
x
j
−
a
i
j
)
2
)
−
1
{\displaystyle f(x_{1},x_{2},...,x_{n-1},x_{n})=\sum _{i=1}^{m}\;\left(c_{i}+\sum \limits _{j=1}^{n}(x_{j}-a_{ij})^{2}\right)^{-1}}
−
∞
≤
x
i
≤
∞
{\displaystyle -\infty \leq x_{i}\leq \infty }
1
≤
i
≤
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
Test functions for constrained optimization
Name
Plot
Formula
Global minimum
Search domain
Rosenbrock function constrained to a disk[ 11]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
1
−
x
)
2
+
100
(
y
−
x
2
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=(1-x)^{2}+100(y-x^{2})^{2}}
subjected to:
x
2
+
y
2
≤
2
{\displaystyle x^{2}+y^{2}\leq 2}
f
(
1.0
,
1.0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(1.0,1.0)=0}
−
1.5
≤
x
≤
1.5
{\displaystyle -1.5\leq x\leq 1.5}
−
1.5
≤
y
≤
1.5
{\displaystyle -1.5\leq y\leq 1.5}
Mishra's Bird function - constrained[ 12] [ 13]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
sin
(
y
)
e
[
(
1
−
cos
x
)
2
]
+
cos
(
x
)
e
[
(
1
−
sin
y
)
2
]
+
(
x
−
y
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin(y)e^{\left[(1-\cos x)^{2}\right]}+\cos(x)e^{\left[(1-\sin y)^{2}\right]}+(x-y)^{2}}
subjected to:
(
x
+
5
)
2
+
(
y
+
5
)
2
<
25
{\displaystyle (x+5)^{2}+(y+5)^{2}<25}
f
(
−
3.1302468
,
−
1.5821422
)
=
−
106.7645367
{\displaystyle f(-3.1302468,-1.5821422)=-106.7645367}
−
10
≤
x
≤
0
{\displaystyle -10\leq x\leq 0}
−
6.5
≤
y
≤
0
{\displaystyle -6.5\leq y\leq 0}
Townsend function (modified)[ 14]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
−
[
cos
(
(
x
−
0.1
)
y
)
]
2
−
x
sin
(
3
x
+
y
)
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-[\cos((x-0.1)y)]^{2}-x\sin(3x+y)}
subjected to:
x
2
+
y
2
<
[
2
cos
t
−
1
2
cos
2
t
−
1
4
cos
3
t
−
1
8
cos
4
t
]
2
+
[
2
sin
t
]
2
{\displaystyle x^{2}+y^{2}<\left[2\cos t-{\frac {1}{2}}\cos 2t-{\frac {1}{4}}\cos 3t-{\frac {1}{8}}\cos 4t\right]^{2}+[2\sin t]^{2}}
t = Atan2(x,y)
f
(
2.0052938
,
1.1944509
)
=
−
2.0239884
{\displaystyle f(2.0052938,1.1944509)=-2.0239884}
−
2.25
≤
x
≤
2.25
{\displaystyle -2.25\leq x\leq 2.25}
−
2.5
≤
y
≤
1.75
{\displaystyle -2.5\leq y\leq 1.75}
Keane's bump function [ 15]
f
(
x
)
=
−
|
[
∑
i
=
1
m
cos
4
(
x
i
)
−
2
∏
i
=
1
m
cos
2
(
x
i
)
]
(
∑
i
=
1
m
i
x
i
2
)
0.5
|
{\displaystyle f(x)=-\left|{\frac {\left[\sum _{i=1}^{m}\cos ^{4}(x_{i})-2\prod _{i=1}^{m}\cos ^{2}(x_{i})\right]}{{\left(\sum _{i=1}^{m}ix_{i}^{2}\right)}^{0.5}}}\right|}
subjected to:
0.75
−
∏
i
=
1
m
x
i
<
0
{\displaystyle 0.75-\prod _{i=1}^{m}x_{i}<0}
∑
i
=
1
m
x
i
−
7.5
m
<
0
{\displaystyle \sum _{i=1}^{m}x_{i}-7.5m<0}
f
(
(
1.60025376
,
0.468675907
)
)
=
−
0.364979746
{\displaystyle f((1.60025376,0.468675907))=-0.364979746}
0
<
x
i
<
10
{\displaystyle 0<x_{i}<10}
Test functions for multi-objective optimization [further explanation needed
Name
Plot
Functions
Constraints
Search domain
Binh and Korn function :[ 5]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
4
x
2
+
4
y
2
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
−
5
)
2
+
(
y
−
5
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)=4x^{2}+4y^{2}\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)=\left(x-5\right)^{2}+\left(y-5\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
−
5
)
2
+
y
2
≤
25
g
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
−
8
)
2
+
(
y
+
3
)
2
≥
7.7
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)=\left(x-5\right)^{2}+y^{2}\leq 25\\g_{2}\left(x,y\right)=\left(x-8\right)^{2}+\left(y+3\right)^{2}\geq 7.7\\\end{cases}}}
0
≤
x
≤
5
{\displaystyle 0\leq x\leq 5}
0
≤
y
≤
3
{\displaystyle 0\leq y\leq 3}
Chankong and Haimes function :[ 16]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
2
+
(
x
−
2
)
2
+
(
y
−
1
)
2
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
9
x
−
(
y
−
1
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)=2+\left(x-2\right)^{2}+\left(y-1\right)^{2}\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)=9x-\left(y-1\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
2
+
y
2
≤
225
g
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
−
3
y
+
10
≤
0
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)=x^{2}+y^{2}\leq 225\\g_{2}\left(x,y\right)=x-3y+10\leq 0\\\end{cases}}}
−
20
≤
x
,
y
≤
20
{\displaystyle -20\leq x,y\leq 20}
Fonseca–Fleming function :[ 17]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
1
−
exp
[
−
∑
i
=
1
n
(
x
i
−
1
n
)
2
]
f
2
(
x
)
=
1
−
exp
[
−
∑
i
=
1
n
(
x
i
+
1
n
)
2
]
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1-\exp \left[-\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left(x_{i}-{\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)^{2}\right]\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1-\exp \left[-\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left(x_{i}+{\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)^{2}\right]\\\end{cases}}}
−
4
≤
x
i
≤
4
{\displaystyle -4\leq x_{i}\leq 4}
1
≤
i
≤
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
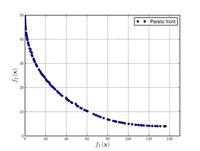
Test function 4:[ 6]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
2
−
y
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
−
0.5
x
−
y
−
1
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)=x^{2}-y\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)=-0.5x-y-1\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
6.5
−
x
6
−
y
≥
0
g
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
7.5
−
0.5
x
−
y
≥
0
g
3
(
x
,
y
)
=
30
−
5
x
−
y
≥
0
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)=6.5-{\frac {x}{6}}-y\geq 0\\g_{2}\left(x,y\right)=7.5-0.5x-y\geq 0\\g_{3}\left(x,y\right)=30-5x-y\geq 0\\\end{cases}}}
−
7
≤
x
,
y
≤
4
{\displaystyle -7\leq x,y\leq 4}
Kursawe function :[ 18]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
∑
i
=
1
2
[
−
10
exp
(
−
0.2
x
i
2
+
x
i
+
1
2
)
]
f
2
(
x
)
=
∑
i
=
1
3
[
|
x
i
|
0.8
+
5
sin
(
x
i
3
)
]
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=\sum _{i=1}^{2}\left[-10\exp \left(-0.2{\sqrt {x_{i}^{2}+x_{i+1}^{2}}}\right)\right]\\&\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=\sum _{i=1}^{3}\left[\left|x_{i}\right|^{0.8}+5\sin \left(x_{i}^{3}\right)\right]\\\end{cases}}}
−
5
≤
x
i
≤
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x_{i}\leq 5}
1
≤
i
≤
3
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 3}
Schaffer function N. 1:[ 19]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
2
f
2
(
x
)
=
(
x
−
2
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x\right)=x^{2}\\f_{2}\left(x\right)=\left(x-2\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
−
A
≤
x
≤
A
{\displaystyle -A\leq x\leq A}
A
{\displaystyle A}
10
{\displaystyle 10}
10
5
{\displaystyle 10^{5}}
A
{\displaystyle A}
Schaffer function N. 2:
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
{
−
x
,
if
x
≤
1
x
−
2
,
if
1
<
x
≤
3
4
−
x
,
if
3
<
x
≤
4
x
−
4
,
if
x
>
4
f
2
(
x
)
=
(
x
−
5
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x\right)={\begin{cases}-x,&{\text{if }}x\leq 1\\x-2,&{\text{if }}1<x\leq 3\\4-x,&{\text{if }}3<x\leq 4\\x-4,&{\text{if }}x>4\\\end{cases}}\\f_{2}\left(x\right)=\left(x-5\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
−
5
≤
x
≤
10
{\displaystyle -5\leq x\leq 10}
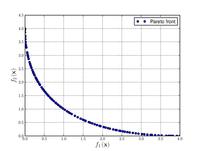
Poloni's two objective function:
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
[
1
+
(
A
1
−
B
1
(
x
,
y
)
)
2
+
(
A
2
−
B
2
(
x
,
y
)
)
2
]
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
+
3
)
2
+
(
y
+
1
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)=\left[1+\left(A_{1}-B_{1}\left(x,y\right)\right)^{2}+\left(A_{2}-B_{2}\left(x,y\right)\right)^{2}\right]\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)=\left(x+3\right)^{2}+\left(y+1\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
where
=
{
A
1
=
0.5
sin
(
1
)
−
2
cos
(
1
)
+
sin
(
2
)
−
1.5
cos
(
2
)
A
2
=
1.5
sin
(
1
)
−
cos
(
1
)
+
2
sin
(
2
)
−
0.5
cos
(
2
)
B
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.5
sin
(
x
)
−
2
cos
(
x
)
+
sin
(
y
)
−
1.5
cos
(
y
)
B
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
1.5
sin
(
x
)
−
cos
(
x
)
+
2
sin
(
y
)
−
0.5
cos
(
y
)
{\displaystyle {\text{where}}={\begin{cases}A_{1}=0.5\sin \left(1\right)-2\cos \left(1\right)+\sin \left(2\right)-1.5\cos \left(2\right)\\A_{2}=1.5\sin \left(1\right)-\cos \left(1\right)+2\sin \left(2\right)-0.5\cos \left(2\right)\\B_{1}\left(x,y\right)=0.5\sin \left(x\right)-2\cos \left(x\right)+\sin \left(y\right)-1.5\cos \left(y\right)\\B_{2}\left(x,y\right)=1.5\sin \left(x\right)-\cos \left(x\right)+2\sin \left(y\right)-0.5\cos \left(y\right)\end{cases}}}
−
π
≤
x
,
y
≤
π
{\displaystyle -\pi \leq x,y\leq \pi }
Zitzler–Deb–Thiele's function N. 1:[ 20]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
1
+
9
29
∑
i
=
2
30
x
i
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
−
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=x_{1}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1+{\frac {9}{29}}\sum _{i=2}^{30}x_{i}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)=1-{\sqrt {\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}}\\\end{cases}}}
0
≤
x
i
≤
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{i}\leq 1}
1
≤
i
≤
30
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 30}
Zitzler–Deb–Thiele's function N. 2:[ 20]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
1
+
9
29
∑
i
=
2
30
x
i
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
−
(
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=x_{1}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1+{\frac {9}{29}}\sum _{i=2}^{30}x_{i}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)=1-\left({\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
0
≤
x
i
≤
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{i}\leq 1}
1
≤
i
≤
30
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 30}
Zitzler–Deb–Thiele's function N. 3:[ 20]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
1
+
9
29
∑
i
=
2
30
x
i
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
−
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
−
(
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
)
sin
(
10
π
f
1
(
x
)
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=x_{1}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1+{\frac {9}{29}}\sum _{i=2}^{30}x_{i}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)=1-{\sqrt {\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}}-\left({\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}\right)\sin \left(10\pi f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\end{cases}}}
0
≤
x
i
≤
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{i}\leq 1}
1
≤
i
≤
30
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 30}
Zitzler–Deb–Thiele's function N. 4:[ 20]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
91
+
∑
i
=
2
10
(
x
i
2
−
10
cos
(
4
π
x
i
)
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
−
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=x_{1}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=91+\sum _{i=2}^{10}\left(x_{i}^{2}-10\cos \left(4\pi x_{i}\right)\right)\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)=1-{\sqrt {\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}}\end{cases}}}
0
≤
x
1
≤
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{1}\leq 1}
−
5
≤
x
i
≤
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x_{i}\leq 5}
2
≤
i
≤
10
{\displaystyle 2\leq i\leq 10}
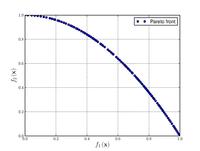
Zitzler–Deb–Thiele's function N. 6:[ 20]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
1
−
exp
(
−
4
x
1
)
sin
6
(
6
π
x
1
)
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
1
+
9
[
∑
i
=
2
10
x
i
9
]
0.25
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
−
(
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1-\exp \left(-4x_{1}\right)\sin ^{6}\left(6\pi x_{1}\right)\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1+9\left[{\frac {\sum _{i=2}^{10}x_{i}}{9}}\right]^{0.25}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)=1-\left({\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
0
≤
x
i
≤
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{i}\leq 1}
1
≤
i
≤
10
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 10}
Osyczka and Kundu function:[ 21]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
−
25
(
x
1
−
2
)
2
−
(
x
2
−
2
)
2
−
(
x
3
−
1
)
2
−
(
x
4
−
4
)
2
−
(
x
5
−
1
)
2
f
2
(
x
)
=
∑
i
=
1
6
x
i
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=-25\left(x_{1}-2\right)^{2}-\left(x_{2}-2\right)^{2}-\left(x_{3}-1\right)^{2}-\left(x_{4}-4\right)^{2}-\left(x_{5}-1\right)^{2}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=\sum _{i=1}^{6}x_{i}^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
−
2
≥
0
g
2
(
x
)
=
6
−
x
1
−
x
2
≥
0
g
3
(
x
)
=
2
−
x
2
+
x
1
≥
0
g
4
(
x
)
=
2
−
x
1
+
3
x
2
≥
0
g
5
(
x
)
=
4
−
(
x
3
−
3
)
2
−
x
4
≥
0
g
6
(
x
)
=
(
x
5
−
3
)
2
+
x
6
−
4
≥
0
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=x_{1}+x_{2}-2\geq 0\\g_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=6-x_{1}-x_{2}\geq 0\\g_{3}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=2-x_{2}+x_{1}\geq 0\\g_{4}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=2-x_{1}+3x_{2}\geq 0\\g_{5}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=4-\left(x_{3}-3\right)^{2}-x_{4}\geq 0\\g_{6}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=\left(x_{5}-3\right)^{2}+x_{6}-4\geq 0\end{cases}}}
0
≤
x
1
,
x
2
,
x
6
≤
10
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{1},x_{2},x_{6}\leq 10}
1
≤
x
3
,
x
5
≤
5
{\displaystyle 1\leq x_{3},x_{5}\leq 5}
0
≤
x
4
≤
6
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{4}\leq 6}
CTP1 function (2 variables):[ 4] [ 22]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
1
+
y
)
exp
(
−
x
1
+
y
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)=x\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)=\left(1+y\right)\exp \left(-{\frac {x}{1+y}}\right)\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
0.858
exp
(
−
0.541
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
)
≥
1
g
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
0.728
exp
(
−
0.295
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
)
≥
1
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)={\frac {f_{2}\left(x,y\right)}{0.858\exp \left(-0.541f_{1}\left(x,y\right)\right)}}\geq 1\\g_{2}\left(x,y\right)={\frac {f_{2}\left(x,y\right)}{0.728\exp \left(-0.295f_{1}\left(x,y\right)\right)}}\geq 1\end{cases}}}
0
≤
x
,
y
≤
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x,y\leq 1}
Constr-Ex problem:[ 4]
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
1
+
y
x
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)=x\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)={\frac {1+y}{x}}\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
y
+
9
x
≥
6
g
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
−
y
+
9
x
≥
1
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)=y+9x\geq 6\\g_{2}\left(x,y\right)=-y+9x\geq 1\\\end{cases}}}
0.1
≤
x
≤
1
{\displaystyle 0.1\leq x\leq 1}
0
≤
y
≤
5
{\displaystyle 0\leq y\leq 5}
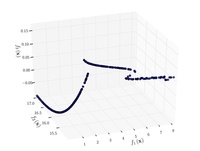
Viennet function:
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.5
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
+
sin
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
3
x
−
2
y
+
4
)
2
8
+
(
x
−
y
+
1
)
2
27
+
15
f
3
(
x
,
y
)
=
1
x
2
+
y
2
+
1
−
1.1
exp
(
−
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)=0.5\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)+\sin \left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)={\frac {\left(3x-2y+4\right)^{2}}{8}}+{\frac {\left(x-y+1\right)^{2}}{27}}+15\\f_{3}\left(x,y\right)={\frac {1}{x^{2}+y^{2}+1}}-1.1\exp \left(-\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right)\\\end{cases}}}
−
3
≤
x
,
y
≤
3
{\displaystyle -3\leq x,y\leq 3}
References
^ Bäck, Thomas (1995). Evolutionary algorithms in theory and practice : evolution strategies, evolutionary programming, genetic algorithms . Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 328. ISBN 978-0-19-509971-3 ^ Haupt, Randy L. Haupt, Sue Ellen (2004). Practical genetic algorithms with CD-Rom (2nd ed.). New York: J. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-45565-3 {{cite book }}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link )^ Oldenhuis, Rody. "Many test functions for global optimizers" . Mathworks. Retrieved 1 November 2012 . ^ a b c d e Deb, Kalyanmoy (2002) Multiobjective optimization using evolutionary algorithms (Repr. ed.). Chichester [u.a.]: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-87339-X .
^ a b Binh T. and Korn U. (1997) MOBES: A Multiobjective Evolution Strategy for Constrained Optimization Problems . In: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Genetic Algorithms. Czech Republic. pp. 176–182
^ a b c Binh T. (1999) A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. The study cases. Technical report. Institute for Automation and Communication. Barleben, Germany
^ Deb K. (2011) Software for multi-objective NSGA-II code in C. Available at URL: https://www.iitk.ac.in/kangal/codes.shtml
^ Ortiz, Gilberto A. "Multi-objective optimization using ES as Evolutionary Algorithm" . Mathworks. Retrieved 1 November 2012 . ^ Whitley, Darrell; Rana, Soraya; Dzubera, John; Mathias, Keith E. (1996). "Evaluating evolutionary algorithms" . Artificial Intelligence . 85 (1– 2). Elsevier BV: 264. doi :10.1016/0004-3702(95)00124-7 ISSN 0004-3702 . ^ Vanaret C. (2015) Hybridization of interval methods and evolutionary algorithms for solving difficult optimization problems. PhD thesis. Ecole Nationale de l'Aviation Civile. Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse, France.
^ "Solve a Constrained Nonlinear Problem - MATLAB & Simulink" . www.mathworks.com . Retrieved 2017-08-29 .^ "Bird Problem (Constrained) | Phoenix Integration" . Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2017-08-29 .{{cite web }}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link )^ Mishra, Sudhanshu (2006). "Some new test functions for global optimization and performance of repulsive particle swarm method" . MPRA Paper . ^ Townsend, Alex (January 2014). "Constrained optimization in Chebfun" . chebfun.org . Retrieved 2017-08-29 . ^ Mishra, Sudhanshu (5 May 2007). "Minimization of Keane's Bump Function by the Repulsive Particle Swarm and the Differential Evolution Methods" . MPRA Paper . University Library of Munich, Germany. ^ Chankong, Vira; Haimes, Yacov Y. (1983). Multiobjective decision making. Theory and methodology . North Holland. ISBN 0-444-00710-5 ^ Fonseca, C. M.; Fleming, P. J. (1995). "An Overview of Evolutionary Algorithms in Multiobjective Optimization". Evol Comput 3 (1): 1– 16. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.50.7779 doi :10.1162/evco.1995.3.1.1 . S2CID 8530790 . ^ F. Kursawe, “A variant of evolution strategies for vector optimization ,” in PPSN I, Vol 496 Lect Notes in Comput Sc. Springer-Verlag, 1991, pp. 193–197.
^ Schaffer, J. David (1984). "Multiple Objective Optimization with Vector Evaluated Genetic Algorithms". In G.J.E Grefensette; J.J. Lawrence Erlbraum (eds.). Proceedings of the First International Conference on Genetic Algorithms . OCLC 20004572 . ^ a b c d e Deb, Kalyan; Thiele, L.; Laumanns, Marco; Zitzler, Eckart (2002). "Scalable multi-objective optimization test problems". Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation. CEC'02 (Cat. No.02TH8600) . Vol. 1. pp. 825– 830. doi :10.1109/CEC.2002.1007032 . ISBN 0-7803-7282-4 S2CID 61001583 . ^ Osyczka, A.; Kundu, S. (1 October 1995). "A new method to solve generalized multicriteria optimization problems using the simple genetic algorithm". Structural Optimization . 10 (2): 94– 99. doi :10.1007/BF01743536 . ISSN 1615-1488 . S2CID 123433499 . ^ Jimenez, F.; Gomez-Skarmeta, A. F.; Sanchez, G.; Deb, K. (May 2002). "An evolutionary algorithm for constrained multi-objective optimization". Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation. CEC'02 (Cat. No.02TH8600) . Vol. 2. pp. 1133– 1138. doi :10.1109/CEC.2002.1004402 . ISBN 0-7803-7282-4 S2CID 56563996 .
External links

![{\displaystyle f(\mathbf {x} )=An+\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left[x_{i}^{2}-A\cos(2\pi x_{i})\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1aa1c38ee739ca9cf4582867d74d469df4676cbc)




![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-20\exp \left[-0.2{\sqrt {0.5\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7f00d1325d65d088f8ae6a96137e62021107921d)
![{\displaystyle -\exp \left[0.5\left(\cos 2\pi x+\cos 2\pi y\right)\right]+e+20}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/565ef43958a50fb0ef473bdd46e30bfc725604a7)








![{\displaystyle f({\boldsymbol {x}})=\sum _{i=1}^{n-1}\left[100\left(x_{i+1}-x_{i}^{2}\right)^{2}+\left(1-x_{i}\right)^{2}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/64863353dcdea2f0ed049cec3aea0a4284d4916a)







![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\left[1+\left(x+y+1\right)^{2}\left(19-14x+3x^{2}-14y+6xy+3y^{2}\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2d020ed324ff07759faf17591157771b0e2cdf07)
![{\displaystyle \left[30+\left(2x-3y\right)^{2}\left(18-32x+12x^{2}+48y-36xy+27y^{2}\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/32e562da4f3219f9d66e059441c59e1d299e8557)






























![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-0.0001\left[\left|\sin x\sin y\exp \left(\left|100-{\frac {\sqrt {x^{2}+y^{2}}}{\pi }}\right|\right)\right|+1\right]^{0.1}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d591ae9bcf2feae162cd00398d78bb6870c82946)














![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.5+{\frac {\sin ^{2}\left(x^{2}-y^{2}\right)-0.5}{\left[1+0.001\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right]^{2}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/995008c6f10a14b44dac568cc544efb7d5ddd631)

![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.5+{\frac {\cos ^{2}\left[\sin \left(\left|x^{2}-y^{2}\right|\right)\right]-0.5}{\left[1+0.001\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right]^{2}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2458c352c0c0524648d8ef713bcea4e80df32fd8)















![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin(y)e^{\left[(1-\cos x)^{2}\right]}+\cos(x)e^{\left[(1-\sin y)^{2}\right]}+(x-y)^{2}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7987d4a794d861e7ccd0795265841d3ca172cfae)





![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-[\cos((x-0.1)y)]^{2}-x\sin(3x+y)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8dac25f97d0b720512d72c313000d5fb5c7d033a)
![{\displaystyle x^{2}+y^{2}<\left[2\cos t-{\frac {1}{2}}\cos 2t-{\frac {1}{4}}\cos 3t-{\frac {1}{8}}\cos 4t\right]^{2}+[2\sin t]^{2}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/57168b192e685c6144e3a9527b12087ac7cb11b4)




![{\displaystyle f(x)=-\left|{\frac {\left[\sum _{i=1}^{m}\cos ^{4}(x_{i})-2\prod _{i=1}^{m}\cos ^{2}(x_{i})\right]}{{\left(\sum _{i=1}^{m}ix_{i}^{2}\right)}^{0.5}}}\right|}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ccc21163c943b12486056d8e1a99a67061277829)













![{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1-\exp \left[-\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left(x_{i}-{\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)^{2}\right]\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1-\exp \left[-\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left(x_{i}+{\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)^{2}\right]\\\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3113203c5d455e0e1e6397d57094e80e527b34ba)

![Test function 4.[6]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3c/Test_function_4_-_Binh.pdf/page1-200px-Test_function_4_-_Binh.pdf.jpg)




![{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=\sum _{i=1}^{2}\left[-10\exp \left(-0.2{\sqrt {x_{i}^{2}+x_{i+1}^{2}}}\right)\right]\\&\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=\sum _{i=1}^{3}\left[\left|x_{i}\right|^{0.8}+5\sin \left(x_{i}^{3}\right)\right]\\\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/aeb9856144d9869aae4254892ece0fe894dfc152)










![{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)=\left[1+\left(A_{1}-B_{1}\left(x,y\right)\right)^{2}+\left(A_{2}-B_{2}\left(x,y\right)\right)^{2}\right]\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)=\left(x+3\right)^{2}+\left(y+1\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9ee5df22af124899c1e268325017ea64e517b51e)














![{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1-\exp \left(-4x_{1}\right)\sin ^{6}\left(6\pi x_{1}\right)\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)=1+9\left[{\frac {\sum _{i=2}^{10}x_{i}}{9}}\right]^{0.25}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)=1-\left({\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f03bdd2b0c7a5af33b0a0fc385f9a9c021635d6e)







![CTP1 function (2 variables).[4]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/CTP1_function_%282_variables%29.pdf/page1-200px-CTP1_function_%282_variables%29.pdf.jpg)



![Constr-Ex problem.[4]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6f/Constr-Ex_problem.pdf/page1-200px-Constr-Ex_problem.pdf.jpg)