Western Bloc
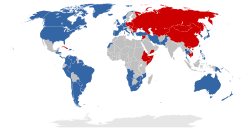 First World: Countries aligned with the Western Bloc (i.e., NATO and allies), led by the United States Second World: Countries aligned with the Eastern Bloc (i.e., Warsaw Pact, China, and allies), led by the Soviet Union  The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, the Freedom Bloc, the Free Bloc, and the American Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of countries that were officially allied with the United States during the Cold War (1947–1991). While the NATO member states, in Western Europe and Northern America, were pivotal to the bloc, it included many other countries, in the broader Asia-Pacific region, the Middle East, Latin America, and Africa with histories of anti-Soviet, anti-communist and, in some cases anti-socialist, ideologies and policies. As such, the bloc was opposed to the political systems and foreign policies of communist countries, which were centered on the Soviet Union, other members of the Warsaw Pact, and usually the People's Republic of China. The name "Western Bloc" emerged in response to and as the antithesis of its communist counterpart, the Eastern Bloc. Throughout the Cold War, the governments and the Western media were more inclined to refer to themselves as the "Free World" or the "First World", whereas the Eastern bloc was often referred to as the "Communist World" or less commonly the "Second World". 1947–1991 Western Bloc associations
* Indicates founding member state
METO, Baghdad Pact, CENTO (until 1979)
SEATO (until 1977)
Latin America and the Caribbean
Middle East/North Africa Region
East and South Asia
OceaniaSub-Saharan Africa
OthersPost-1991 Western-aligned associations
* Indicates pre-1991 member state Major non-NATO ally (MNNAs)
Middle Eastern PartnersAsia-Pacific and Oceania PartnersInter-American PartnersPacific Squad, G7, C12, and Quadrilateral Security DialogueOthers
See alsoNotesSources
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia













