피리딘
Pyridine
 Full structural formula of pyridine Full structural formula of pyridine
|
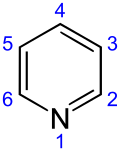 Skeletal formula of pyridine, showing the numbering convention Skeletal formula of pyridine, showing the numbering convention
|
|
 Ball-and-stick diagram of pyridine Ball-and-stick diagram of pyridine
|
 Space-filling model of pyridine Space-filling model of pyridine
|
|

|
| 이름
|
| 우선명 (PIN)
|
| 체계명
|
| 별칭
Azine
Azinine
1-Azacyclohexa-1,3,5-diene
|
| 식별자
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ChEBI
|
|
| ChEMBL
|
|
| ChemSpider
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard
|
100.003.464
|
| EC 번호
|
|
| KEGG
|
|
|
|
|
| UNII
|
|
|
|
|
InChI=1S/C5H5N/c1-2-4-6-5-3-1/h1-5H  예 예Key: JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N  예 예InChI=1/C5H5N/c1-2-4-6-5-3-1/h1-5H Key: JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYAY
|
|
|
| 성질
|
|
|
C5H5N
|
| 몰 질량
|
79.102 g·mol−1
|
| 겉보기
|
Colorless liquid[2]
|
| 냄새
|
Nauseating, fish-like[3]
|
| 밀도
|
0.9819 g/mL[4]
|
| 녹는점
|
−41.6 °C (−42.9 °F; 231.6 K)
|
| 끓는점
|
115.2 °C (239.4 °F; 388.3 K)
|
|
|
Miscible
|
| log P
|
0.73[5]
|
| 증기 압력
|
16 mmHg (20 °C)[3]
|
| 짝산
|
Pyridinium
|
|
|
1.5093
|
| 점도
|
0.88 cP 25 °C
|
|
|
2.2 D[6]
|
| 위험[8]
|
|
|
Flammable (F)
Harmful (Xn)
|
| R-phrases (outdated)
|
R20 R21 R22 R34 R36 R38
|
| NFPA 704 (파이어 다이아몬드)
|
|
| 인화점
|
21 °C (70 °F; 294 K)
|
| 폭발 한계
|
1.8–12.4%[3]
|
|
|
5 ppm (TWA)
|
| 반수 치사량 또는 반수 치사농도 (LD, LC):
|
|
|
891 mg/kg (rat, oral)
1500 mg/kg (mouse, oral)
1580 mg/kg (rat, oral)[7]
|
|
|
9000 ppm (rat, 1 hr)[7]
|
| NIOSH (미국 건강 노출 한계):
|
|
|
TWA 5 ppm (15 mg/m3)[3]
|
|
|
TWA 5 ppm (15 mg/m3)[3]
|
|
|
1000 ppm[3]
|
| 관련 화합물
|
|
|
Picoline
Quinoline
|
관련 화합물
|
Aniline
피리미딘
Piperidine
|
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.
|
피리딘(Pyridine)은 벤젠의 CH 하나가 질소로 치환된 헤테로고리 화합물이다.
형성
 아세트알데히드와 포름알데히드로부터 아크롤레인을 형성 아세트알데히드와 포름알데히드로부터 아크롤레인을 형성
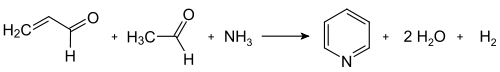 아크롤레인과 아세트알데히드로부터 피리딘을 응결 아크롤레인과 아세트알데히드로부터 피리딘을 응결
역사
피리딘 불순물은 동물의 뼈와 기타 유기 물질을 가열함으로써 초기 연금술사들에 의해 만들어졌지만,[9] 최초의 문서화된 기록은 스코틀랜드의 과학자 토머스 앤더슨에 의해 이루어졌다.[10][11]
각주
- ↑ 《Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book)》. Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. 141쪽. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Shimizu, S.; Watanabe, N.; Kataoka, T.; Shoji, T.; Abe, N.; Morishita, S.; Ichimura, H., 〈Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives〉, 《울만 공업화학 백과사전(Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry)》, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_399
- ↑ 가 나 다 라 마 바 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. “#0541”. 미국 국립 직업안전위생연구소 (NIOSH).
- ↑ Lide, p. 3–474
- ↑ “Pyridine - CAS#:110-86-1”. 《ChemSrc》. 2020년 1월 8일.
- ↑ 《RÖMPP Online – Version 3.5》. 《Thieme Chemistry》 (Stuttgart: Georg Thieme). 2009.
- ↑ 가 나 “Pyridine”. 《Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH)》. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ “Pyridine MSDS”. 《fishersci.com》. Fisher. 2010년 6월 11일에 원본 문서에서 보존된 문서. 2020년 10월 3일에 확인함.
- ↑ Weissberger, A.; Klingberg, A.; Barnes, R. A.; Brody, F.; Ruby, P.R. (1960). 《Pyridine and its Derivatives》 1. New York: Interscience.
- ↑ Anderson, Thomas (1849). “On the constitution and properties of picoline, a new organic base from coal-tar”. 《Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh》 16: 123–136.
- ↑ Anderson, T. (1849). “Producte der trocknen Destillation thierischer Materien” [Products of the dry distillation of animal matter]. 《Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie》 (독일어) 70: 32–38. doi:10.1002/jlac.18490700105.
외부 링크
 위키미디어 공용에 피리딘 관련 미디어 분류가 있습니다. 위키미디어 공용에 피리딘 관련 미디어 분류가 있습니다.
|





















