–Ę–Ķ—Ā—ā–ĺ–≤—č–Ķ —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł–ł –ī–Ľ—Ź –ĺ–Ņ—ā–ł–ľ–ł–∑–į—Ü–ł–ł –í –Ņ—Ä–ł–ļ–Ľ–į–ī–Ĺ–ĺ–Ļ –ľ–į—ā–Ķ–ľ–į—ā–ł–ļ–Ķ, —ā–Ķ—Ā—ā–ĺ–≤—č–Ķ —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł–ł , –ł–∑–≤–Ķ—Ā—ā–Ĺ—č–Ķ –ļ–į–ļ –ł—Ā–ļ—É—Ā—Ā—ā–≤–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—č–Ķ –Ľ–į–Ĺ–ī—ą–į—Ą—ā—č , —Ź–≤–Ľ—Ź—é—ā—Ā—Ź –Ņ–ĺ–Ľ–Ķ–∑–Ĺ—č–ľ–ł –ī–Ľ—Ź –ĺ—Ü–Ķ–Ĺ–ļ–ł —Ö–į—Ä–į–ļ—ā–Ķ—Ä–ł—Ā—ā–ł–ļ –į–Ľ–≥–ĺ—Ä–ł—ā–ľ–ĺ–≤ –ĺ–Ņ—ā–ł–ľ–ł–∑–į—Ü–ł–ł, —ā–į–ļ–ł—Ö –ļ–į–ļ:
–°–ļ–ĺ—Ä–ĺ—Ā—ā—Ć —Ā—Ö–ĺ–ī–ł–ľ–ĺ—Ā—ā–ł.
–Ę–ĺ—á–Ĺ–ĺ—Ā—ā—Ć.
–†–ĺ–Ī–į—Ā—ā–Ĺ–ĺ—Ā—ā—Ć .–ě–Ī—Č–į—Ź –Ņ—Ä–ĺ–ł–∑–≤–ĺ–ī–ł—ā–Ķ–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ–ĺ—Ā—ā—Ć. –í —Ā—ā–į—ā—Ć–Ķ –Ņ—Ä–Ķ–ī—Ā—ā–į–≤–Ľ–Ķ–Ĺ—č –Ĺ–Ķ–ļ–ĺ—ā–ĺ—Ä—č–Ķ —ā–Ķ—Ā—ā–ĺ–≤—č–Ķ —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł–ł —Ā —Ü–Ķ–Ľ—Ć—é –ī–į—ā—Ć –Ņ—Ä–Ķ–ī—Ā—ā–į–≤–Ľ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ķ –ĺ —Ä–į–∑–Ľ–ł—á–Ĺ—č—Ö —Ā–ł—ā—É–į—Ü–ł—Ź—Ö, —Ā –ļ–ĺ—ā–ĺ—Ä—č–ľ–ł –Ņ—Ä–ł—Ö–ĺ–ī–ł—ā—Ā—Ź —Ā—ā–į–Ľ–ļ–ł–≤–į—ā—Ć—Ā—Ź –Ņ—Ä–ł –Ņ—Ä–Ķ–ĺ–ī–ĺ–Ľ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–ł –Ņ–ĺ–ī–ĺ–Ī–Ĺ—č—Ö –Ņ—Ä–ĺ–Ī–Ľ–Ķ–ľ.
–í —Ā—ā–į—ā—Ć–Ķ –Ņ—Ä–Ķ–ī—Ā—ā–į–≤–Ľ–Ķ–Ĺ—č –ĺ–Ī—Č–į—Ź —Ą–ĺ—Ä–ľ—É–Ľ–į —É—Ä–į–≤–Ĺ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł—Ź, —É—á–į—Ā—ā–ĺ–ļ —Ü–Ķ–Ľ–Ķ–≤–ĺ–Ļ —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł–ł, –≥—Ä–į–Ĺ–ł—Ü—č –Ņ–Ķ—Ä–Ķ–ľ–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—č—Ö –ł –ļ–ĺ–ĺ—Ä–ī–ł–Ĺ–į—ā—č –≥–Ľ–ĺ–Ī–į–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ–ĺ–≥–ĺ –ľ–ł–Ĺ–ł–ľ—É–ľ–į.
–Ě–į–∑–≤–į–Ĺ–ł–Ķ
–†–ł—Ā—É–Ĺ–ĺ–ļ
–§–ĺ—Ä–ľ—É–Ľ–į
–ď–Ľ–ĺ–Ī–į–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ—č–Ļ –ľ–ł–Ĺ–ł–ľ—É–ľ
–ú–Ķ—ā–ĺ–ī –Ņ–ĺ–ł—Ā–ļ–į
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –†–į—Ā—ā—Ä–ł–≥–ł–Ĺ–į
f
(
x
)
=
A
n
+
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
n
[
x
i
2
‚ąí
A
cos
‚Ā°
(
2
ŌÄ
x
i
)
]
{\displaystyle f(\mathbf {x} )=An+\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left[x_{i}^{2}-A\cos(2\pi x_{i})\right]}
where:
A
=
10
{\displaystyle {\text{where: }}A=10}
f
(
0
,
…
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,\dots ,0)=0}
‚ąí
5.12
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
5.12
{\displaystyle -5.12\leq x_{i}\leq 5.12}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –≠–ļ–Ľ–ł [–į–Ĺ–≥–Ľ.]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
‚ąí
20
exp
‚Ā°
[
‚ąí
0.2
0.5
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
]
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-20\exp \left[-0.2{\sqrt {0.5\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)}}\right]}
‚ąí
exp
‚Ā°
[
0.5
(
cos
‚Ā°
(
2
ŌÄ
x
)
+
cos
‚Ā°
(
2
ŌÄ
y
)
)
]
+
e
+
20
{\displaystyle -\exp \left[0.5\left(\cos(2\pi x)+\cos(2\pi y)\right)\right]+e+20}
f
(
0
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,0)=0}
‚ąí
5
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x,y\leq 5}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź —Ā—Ą–Ķ—Ä—č
f
(
x
)
=
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
n
x
i
2
{\displaystyle f({\boldsymbol {x}})=\sum _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}^{2}}
f
(
x
1
,
…
,
x
n
)
=
f
(
0
,
…
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(x_{1},\dots ,x_{n})=f(0,\dots ,0)=0}
‚ąí
‚ąě
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
‚ąě
{\displaystyle -\infty \leq x_{i}\leq \infty }
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
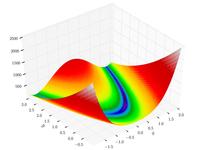
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –†–ĺ–∑–Ķ–Ĺ–Ī—Ä–ĺ–ļ–į
f
(
x
)
=
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
n
‚ąí
1
[
100
(
x
i
+
1
‚ąí
x
i
2
)
2
+
(
x
i
‚ąí
1
)
2
]
{\displaystyle f({\boldsymbol {x}})=\sum _{i=1}^{n-1}\left[100\left(x_{i+1}-x_{i}^{2}\right)^{2}+\left(x_{i}-1\right)^{2}\right]}
Min
=
{
n
=
2
‚Üí
f
(
1
,
1
)
=
0
,
n
=
3
‚Üí
f
(
1
,
1
,
1
)
=
0
,
n
>
3
‚Üí
f
(
1
,
…
,
1
‚Źü
n
times
)
=
0
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}n=2&\rightarrow \quad f(1,1)=0,\\n=3&\rightarrow \quad f(1,1,1)=0,\\n>3&\rightarrow \quad f(\underbrace {1,\dots ,1} _{n{\text{ times}}})=0\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
‚ąě
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
‚ąě
{\displaystyle -\infty \leq x_{i}\leq \infty }
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –Ď–ł–Ľ–į
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
1.5
‚ąí
x
+
x
y
)
2
+
(
2.25
‚ąí
x
+
x
y
2
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\left(1.5-x+xy\right)^{2}+\left(2.25-x+xy^{2}\right)^{2}}
+
(
2.625
‚ąí
x
+
x
y
3
)
2
{\displaystyle +\left(2.625-x+xy^{3}\right)^{2}}
f
(
3
,
0.5
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(3,0.5)=0}
‚ąí
4.5
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
4.5
{\displaystyle -4.5\leq x,y\leq 4.5}
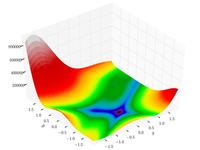
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ď–ĺ–Ľ—Ć–ī—ą–Ķ–Ļ–Ĺ–į-–ü—Ä–į–Ļ—Ā–į
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
[
1
+
(
x
+
y
+
1
)
2
(
19
‚ąí
14
x
+
3
x
2
‚ąí
14
y
+
6
x
y
+
3
y
2
)
]
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\left[1+\left(x+y+1\right)^{2}\left(19-14x+3x^{2}-14y+6xy+3y^{2}\right)\right]}
[
30
+
(
2
x
‚ąí
3
y
)
2
(
18
‚ąí
32
x
+
12
x
2
+
48
y
‚ąí
36
x
y
+
27
y
2
)
]
{\displaystyle \left[30+\left(2x-3y\right)^{2}\left(18-32x+12x^{2}+48y-36xy+27y^{2}\right)\right]}
f
(
0
,
‚ąí
1
)
=
3
{\displaystyle f(0,-1)=3}
‚ąí
2
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
2
{\displaystyle -2\leq x,y\leq 2}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –Ď—É—ā–į
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
+
2
y
‚ąí
7
)
2
+
(
2
x
+
y
‚ąí
5
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\left(x+2y-7\right)^{2}+\left(2x+y-5\right)^{2}}
f
(
1
,
3
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(1,3)=0}
‚ąí
10
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
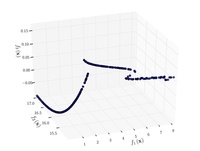
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –Ď—É–ļ–ł–Ĺ–į N 6
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
100
|
y
‚ąí
0.01
x
2
|
+
0.01
|
x
+
10
|
.
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=100{\sqrt {\left|y-0.01x^{2}\right|}}+0.01\left|x+10\right|.\quad }
f
(
‚ąí
10
,
1
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(-10,1)=0}
‚ąí
15
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
‚ąí
5
{\displaystyle -15\leq x\leq -5}
‚ąí
3
‚ȧ
y
‚ȧ
3
{\displaystyle -3\leq y\leq 3}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ú–į—ā—Ć—Ź—Ā–į
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.26
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
‚ąí
0.48
x
y
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.26\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)-0.48xy}
f
(
0
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,0)=0}
‚ąí
10
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –õ–Ķ–≤–ł N 13
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
sin
2
‚Ā°
3
ŌÄ
x
+
(
x
‚ąí
1
)
2
(
1
+
sin
2
‚Ā°
3
ŌÄ
y
)
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin ^{2}3\pi x+\left(x-1\right)^{2}\left(1+\sin ^{2}3\pi y\right)}
+
(
y
‚ąí
1
)
2
(
1
+
sin
2
‚Ā°
2
ŌÄ
y
)
{\displaystyle +\left(y-1\right)^{2}\left(1+\sin ^{2}2\pi y\right)}
f
(
1
,
1
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(1,1)=0}
‚ąí
10
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –•–ł–ľ–ľ–Ķ–Ľ—Ć–Ī–Ľ–į—É
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
2
+
y
‚ąí
11
)
2
+
(
x
+
y
2
‚ąí
7
)
2
.
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=(x^{2}+y-11)^{2}+(x+y^{2}-7)^{2}.\quad }
Min
=
{
f
(
3.0
,
2.0
)
=
0.0
f
(
‚ąí
2.805118
,
3.131312
)
=
0.0
f
(
‚ąí
3.779310
,
‚ąí
3.283186
)
=
0.0
f
(
3.584428
,
‚ąí
1.848126
)
=
0.0
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}f\left(3.0,2.0\right)&=0.0\\f\left(-2.805118,3.131312\right)&=0.0\\f\left(-3.779310,-3.283186\right)&=0.0\\f\left(3.584428,-1.848126\right)&=0.0\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
5
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x,y\leq 5}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź —ā—Ä–Ķ—Ö–≥–ĺ—Ä–Ī–ĺ–≥–ĺ –≤–Ķ—Ä–Ī–Ľ—é–ī–į
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
2
x
2
‚ąí
1.05
x
4
+
x
6
6
+
x
y
+
y
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=2x^{2}-1.05x^{4}+{\frac {x^{6}}{6}}+xy+y^{2}}
f
(
0
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,0)=0}
‚ąí
5
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x,y\leq 5}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ė–∑–ĺ–ľ–į
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
‚ąí
cos
‚Ā°
(
x
)
cos
‚Ā°
(
y
)
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
(
(
x
‚ąí
ŌÄ
)
2
+
(
y
‚ąí
ŌÄ
)
2
)
)
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-\cos \left(x\right)\cos \left(y\right)\exp \left(-\left(\left(x-\pi \right)^{2}+\left(y-\pi \right)^{2}\right)\right)}
f
(
ŌÄ
,
ŌÄ
)
=
‚ąí
1
{\displaystyle f(\pi ,\pi )=-1}
‚ąí
100
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
100
{\displaystyle -100\leq x,y\leq 100}
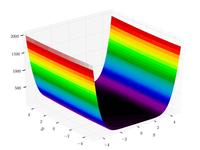
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź "–ļ—Ä–Ķ—Ā—ā –Ĺ–į –Ņ–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–ĺ—Ā–Ķ"
(Cross-in-tray function)
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
‚ąí
0.0001
[
|
sin
‚Ā°
x
sin
‚Ā°
y
exp
‚Ā°
(
|
100
‚ąí
x
2
+
y
2
ŌÄ
|
)
|
+
1
]
0.1
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-0.0001\left[\left|\sin x\sin y\exp \left(\left|100-{\frac {\sqrt {x^{2}+y^{2}}}{\pi }}\right|\right)\right|+1\right]^{0.1}}
Min
=
{
f
(
1.34941
,
‚ąí
1.34941
)
=
‚ąí
2.06261
f
(
1.34941
,
1.34941
)
=
‚ąí
2.06261
f
(
‚ąí
1.34941
,
1.34941
)
=
‚ąí
2.06261
f
(
‚ąí
1.34941
,
‚ąí
1.34941
)
=
‚ąí
2.06261
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}f\left(1.34941,-1.34941\right)&=-2.06261\\f\left(1.34941,1.34941\right)&=-2.06261\\f\left(-1.34941,1.34941\right)&=-2.06261\\f\left(-1.34941,-1.34941\right)&=-2.06261\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
10
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
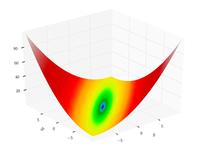
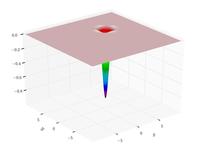
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź "–Ņ–ĺ–ī—Ā—ā–į–≤–ļ–į –ī–Ľ—Ź —Ź–ł—Ü"
(Eggholder function)
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
‚ąí
(
y
+
47
)
sin
‚Ā°
|
x
2
+
(
y
+
47
)
|
‚ąí
x
sin
‚Ā°
|
x
‚ąí
(
y
+
47
)
|
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-\left(y+47\right)\sin {\sqrt {\left|{\frac {x}{2}}+\left(y+47\right)\right|}}-x\sin {\sqrt {\left|x-\left(y+47\right)\right|}}}
f
(
512
,
404.2319
)
=
‚ąí
959.6407
{\displaystyle f(512,404.2319)=-959.6407}
‚ąí
512
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
512
{\displaystyle -512\leq x,y\leq 512}
–Ę–į–Ī–Ľ–ł—á–Ĺ–į—Ź —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –•–ĺ–Ľ—Ć–ī–Ķ—Ä–į
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
‚ąí
|
sin
‚Ā°
x
cos
‚Ā°
y
exp
‚Ā°
(
|
1
‚ąí
x
2
+
y
2
ŌÄ
|
)
|
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-\left|\sin x\cos y\exp \left(\left|1-{\frac {\sqrt {x^{2}+y^{2}}}{\pi }}\right|\right)\right|}
Min
=
{
f
(
8.05502
,
9.66459
)
=
‚ąí
19.2085
f
(
‚ąí
8.05502
,
9.66459
)
=
‚ąí
19.2085
f
(
8.05502
,
‚ąí
9.66459
)
=
‚ąí
19.2085
f
(
‚ąí
8.05502
,
‚ąí
9.66459
)
=
‚ąí
19.2085
{\displaystyle {\text{Min}}={\begin{cases}f\left(8.05502,9.66459\right)&=-19.2085\\f\left(-8.05502,9.66459\right)&=-19.2085\\f\left(8.05502,-9.66459\right)&=-19.2085\\f\left(-8.05502,-9.66459\right)&=-19.2085\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
10
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle -10\leq x,y\leq 10}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ú–į–ļ–ö–ĺ—Ä–ľ–ł–ļ–į
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
sin
‚Ā°
(
x
+
y
)
+
(
x
‚ąí
y
)
2
‚ąí
1.5
x
+
2.5
y
+
1
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin \left(x+y\right)+\left(x-y\right)^{2}-1.5x+2.5y+1}
f
(
‚ąí
0.54719
,
‚ąí
1.54719
)
=
‚ąí
1.9133
{\displaystyle f(-0.54719,-1.54719)=-1.9133}
‚ąí
1.5
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
4
{\displaystyle -1.5\leq x\leq 4}
‚ąí
3
‚ȧ
y
‚ȧ
4
{\displaystyle -3\leq y\leq 4}
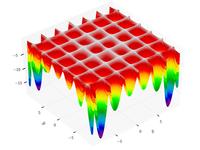
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –®–į—Ą—Ą–Ķ—Ä–į N2
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.5
+
sin
2
‚Ā°
(
x
2
‚ąí
y
2
)
‚ąí
0.5
[
1
+
0.001
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
]
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.5+{\frac {\sin ^{2}\left(x^{2}-y^{2}\right)-0.5}{\left[1+0.001\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right]^{2}}}}
f
(
0
,
0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(0,0)=0}
‚ąí
100
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
100
{\displaystyle -100\leq x,y\leq 100}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –®–į—Ą—Ą–Ķ—Ä–į N4
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.5
+
cos
2
‚Ā°
[
sin
‚Ā°
(
|
x
2
‚ąí
y
2
|
)
]
‚ąí
0.5
[
1
+
0.001
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
]
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.5+{\frac {\cos ^{2}\left[\sin \left(\left|x^{2}-y^{2}\right|\right)\right]-0.5}{\left[1+0.001\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right]^{2}}}}
f
(
0
,
1.25313
)
=
0.292579
{\displaystyle f(0,1.25313)=0.292579}
‚ąí
100
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
100
{\displaystyle -100\leq x,y\leq 100}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –°—ā—č–Ī–ł–Ĺ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–≥–ĺ-–Ę–į–Ĺ–≥–į
f
(
x
)
=
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
n
x
i
4
‚ąí
16
x
i
2
+
5
x
i
2
{\displaystyle f({\boldsymbol {x}})={\frac {\sum _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}^{4}-16x_{i}^{2}+5x_{i}}{2}}}
‚ąí
39.16617
n
<
f
(
‚ąí
2.903534
,
…
,
‚ąí
2.903534
‚Źü
n
times
)
<
‚ąí
39.16616
n
{\displaystyle -39.16617n<f(\underbrace {-2.903534,\ldots ,-2.903534} _{n{\text{ times}}})<-39.16616n}
‚ąí
5
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x_{i}\leq 5}
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
–Ě–į–∑–≤–į–Ĺ–ł–Ķ
–†–ł—Ā—É–Ĺ–ĺ–ļ
–§–ĺ—Ä–ľ—É–Ľ–į
–ď–Ľ–ĺ–Ī–į–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ—č–Ļ –ľ–ł–Ĺ–ł–ľ—É–ľ
–ú–Ķ—ā–ĺ–ī –Ņ–ĺ–ł—Ā–ļ–į
—Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –†–ĺ–∑–Ķ–Ĺ–Ī—Ä–ĺ–ļ–į, –ĺ–≥—Ä–į–Ĺ–ł—á–Ķ–Ĺ–į –ļ—É–Ī–ł—á–Ķ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ļ –ł –Ņ—Ä—Ź–ľ–ĺ–Ļ[ 1]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
1
‚ąí
x
)
2
+
100
(
y
‚ąí
x
2
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=(1-x)^{2}+100(y-x^{2})^{2}}
subjected to:
(
x
‚ąí
1
)
3
‚ąí
y
+
1
<
0
and
x
+
y
‚ąí
2
<
0
{\displaystyle (x-1)^{3}-y+1<0{\text{ and }}x+y-2<0}
f
(
1.0
,
1.0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(1.0,1.0)=0}
‚ąí
1.5
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
1.5
{\displaystyle -1.5\leq x\leq 1.5}
‚ąí
0.5
‚ȧ
y
‚ȧ
2.5
{\displaystyle -0.5\leq y\leq 2.5}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –†–ĺ–∑–Ķ–Ĺ–Ī—Ä–ĺ–ļ–į, –ĺ–≥—Ä–į–Ĺ–ł—á–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ–į—Ź –ī–ł—Ā–ļ–ĺ–ľ[ 2]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
1
‚ąí
x
)
2
+
100
(
y
‚ąí
x
2
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=(1-x)^{2}+100(y-x^{2})^{2}}
subjected to:
x
2
+
y
2
<
2
{\displaystyle x^{2}+y^{2}<2}
f
(
1.0
,
1.0
)
=
0
{\displaystyle f(1.0,1.0)=0}
‚ąí
1.5
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
1.5
{\displaystyle -1.5\leq x\leq 1.5}
‚ąí
1.5
‚ȧ
y
‚ȧ
1.5
{\displaystyle -1.5\leq y\leq 1.5}
–ě–≥—Ä–į–Ĺ–ł—á–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ–į—Ź —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ú–ł—ą—Ä—č-–Ď—Ď—Ä–ī–į[ 3] [ 4]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
sin
‚Ā°
(
y
)
e
[
(
1
‚ąí
cos
‚Ā°
x
)
2
]
+
cos
‚Ā°
(
x
)
e
[
(
1
‚ąí
sin
‚Ā°
y
)
2
]
+
(
x
‚ąí
y
)
2
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin(y)e^{\left[(1-\cos x)^{2}\right]}+\cos(x)e^{\left[(1-\sin y)^{2}\right]}+(x-y)^{2}}
subjected to:
(
x
+
5
)
2
+
(
y
+
5
)
2
<
25
{\displaystyle (x+5)^{2}+(y+5)^{2}<25}
f
(
‚ąí
3.1302468
,
‚ąí
1.5821422
)
=
‚ąí
106.7645367
{\displaystyle f(-3.1302468,-1.5821422)=-106.7645367}
‚ąí
10
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
0
{\displaystyle -10\leq x\leq 0}
‚ąí
6.5
‚ȧ
y
‚ȧ
0
{\displaystyle -6.5\leq y\leq 0}
–ú–ĺ–ī–ł—Ą–ł—Ü–ł—Ä–ĺ–≤–į–Ĺ–Ĺ–į—Ź —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –Ę–į—É—Ā–Ķ–Ĺ–ī–į[ 5]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
‚ąí
[
cos
‚Ā°
(
(
x
‚ąí
0.1
)
y
)
]
2
‚ąí
x
sin
‚Ā°
(
3
x
+
y
)
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-[\cos((x-0.1)y)]^{2}-x\sin(3x+y)}
subjected to:
x
2
+
y
2
<
[
2
cos
‚Ā°
t
‚ąí
1
2
cos
‚Ā°
2
t
‚ąí
1
4
cos
‚Ā°
3
t
‚ąí
1
8
cos
‚Ā°
4
t
]
2
+
[
2
sin
‚Ā°
t
]
2
{\displaystyle x^{2}+y^{2}<\left[2\cos t-{\frac {1}{2}}\cos 2t-{\frac {1}{4}}\cos 3t-{\frac {1}{8}}\cos 4t\right]^{2}+[2\sin t]^{2}}
t = Atan2(x,y)
f
(
2.0052938
,
1.1944509
)
=
‚ąí
2.0239884
{\displaystyle f(2.0052938,1.1944509)=-2.0239884}
‚ąí
2.25
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
2.5
{\displaystyle -2.25\leq x\leq 2.5}
‚ąí
2.5
‚ȧ
y
‚ȧ
1.75
{\displaystyle -2.5\leq y\leq 1.75}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –°–ł–ľ–ł–ĺ–Ĺ–Ķ—Ā–ļ—É[ 6]
f
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.1
x
y
{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.1xy}
subjected to:
x
2
+
y
2
‚ȧ
[
r
T
+
r
S
cos
‚Ā°
(
n
arctan
‚Ā°
x
y
)
]
2
{\displaystyle x^{2}+y^{2}\leq \left[r_{T}+r_{S}\cos \left(n\arctan {\frac {x}{y}}\right)\right]^{2}}
where:
r
T
=
1
,
r
S
=
0.2
and
n
=
8
{\displaystyle {\text{where: }}r_{T}=1,r_{S}=0.2{\text{ and }}n=8}
f
(
¬Ī
0.85586214
,
‚ąď
0.85586214
)
=
‚ąí
0.072625
{\displaystyle f(\pm 0.85586214,\mp 0.85586214)=-0.072625}
‚ąí
1.25
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
1.25
{\displaystyle -1.25\leq x,y\leq 1.25}
–Ě–į–∑–≤–į–Ĺ–ł–Ķ / –†–ł—Ā—É–Ĺ–ĺ–ļ
–§–ĺ—Ä–ľ—É–Ľ–į
–ú–ł–Ĺ–ł–ľ—É–ľ
–ě–Ī–Ľ–į—Ā—ā—Ć –Ņ–ĺ–ł—Ā–ļ–į
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –Ď–ł–Ĺ–į –ł –ö–ĺ—Ä–Ĺ–į
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
4
x
2
+
4
y
2
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
‚ąí
5
)
2
+
(
y
‚ąí
5
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=4x^{2}+4y^{2}\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=\left(x-5\right)^{2}+\left(y-5\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
‚ąí
5
)
2
+
y
2
‚ȧ
25
g
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
‚ąí
8
)
2
+
(
y
+
3
)
2
‚Č•
7.7
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=\left(x-5\right)^{2}+y^{2}\leq 25\\g_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=\left(x-8\right)^{2}+\left(y+3\right)^{2}\geq 7.7\\\end{cases}}}
0
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle 0\leq x\leq 5}
0
‚ȧ
y
‚ȧ
3
{\displaystyle 0\leq y\leq 3}
Chakong and Haimes function
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
2
+
(
x
‚ąí
2
)
2
+
(
y
‚ąí
1
)
2
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
9
x
‚ąí
(
y
‚ąí
1
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=2+\left(x-2\right)^{2}+\left(y-1\right)^{2}\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=9x-\left(y-1\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
2
+
y
2
‚ȧ
225
g
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
‚ąí
3
y
+
10
‚ȧ
0
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=x^{2}+y^{2}\leq 225\\g_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=x-3y+10\leq 0\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
20
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
20
{\displaystyle -20\leq x,y\leq 20}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –§–ĺ–Ĺ—Ā–Ķ–ļ–ł –ł –§–Ľ–Ķ–ľ–ł–Ĺ–≥–į
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
1
‚ąí
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
n
(
x
i
‚ąí
1
n
)
2
)
f
2
(
x
)
=
1
‚ąí
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
n
(
x
i
+
1
n
)
2
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1-\exp \left(-\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left(x_{i}-{\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)^{2}\right)\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1-\exp \left(-\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left(x_{i}+{\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)^{2}\right)\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
4
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
4
{\displaystyle -4\leq x_{i}\leq 4}
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
n
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq n}
Test function 4
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
2
‚ąí
y
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
‚ąí
0.5
x
‚ąí
y
‚ąí
1
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=x^{2}-y\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=-0.5x-y-1\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
6.5
‚ąí
x
6
‚ąí
y
‚Č•
0
g
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
7.5
‚ąí
0.5
x
‚ąí
y
‚Č•
0
g
3
(
x
,
y
)
=
30
‚ąí
5
x
‚ąí
y
‚Č•
0
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=6.5-{\frac {x}{6}}-y\geq 0\\g_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=7.5-0.5x-y\geq 0\\g_{3}\left(x,y\right)&=30-5x-y\geq 0\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
7
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
4
{\displaystyle -7\leq x,y\leq 4}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ö—É—Ä—Ā–į–≤–Ķ
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
2
[
‚ąí
10
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
0.2
x
i
2
+
x
i
+
1
2
)
]
f
2
(
x
)
=
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
3
[
|
x
i
|
0.8
+
5
sin
‚Ā°
(
x
i
3
)
]
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=\sum _{i=1}^{2}\left[-10\exp \left(-0.2{\sqrt {x_{i}^{2}+x_{i+1}^{2}}}\right)\right]\\&\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=\sum _{i=1}^{3}\left[\left|x_{i}\right|^{0.8}+5\sin \left(x_{i}^{3}\right)\right]\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
5
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x_{i}\leq 5}
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
3
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 3}
Schaffer function N. 1
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
2
f
2
(
x
)
=
(
x
‚ąí
2
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x\right)&=x^{2}\\f_{2}\left(x\right)&=\left(x-2\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
A
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
A
{\displaystyle -A\leq x\leq A}
A
{\displaystyle A}
10
{\displaystyle 10}
10
5
{\displaystyle 10^{5}}
A
{\displaystyle A}
Schaffer function N. 2
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
{
‚ąí
x
,
if
x
‚ȧ
1
x
‚ąí
2
,
if
1
<
x
‚ȧ
3
4
‚ąí
x
,
if
3
<
x
‚ȧ
4
x
‚ąí
4
,
if
x
>
4
f
2
(
x
)
=
(
x
‚ąí
5
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x\right)&={\begin{cases}-x,&{\text{if }}x\leq 1\\x-2,&{\text{if }}1<x\leq 3\\4-x,&{\text{if }}3<x\leq 4\\x-4,&{\text{if }}x>4\\\end{cases}}\\f_{2}\left(x\right)&=\left(x-5\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
5
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle -5\leq x\leq 10}
–ě–Ī—ä–Ķ–ļ—ā–ł–≤–Ĺ–į—Ź —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ü–ĺ–Ľ–ĺ–Ĺ–ł2
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
[
1
+
(
A
1
‚ąí
B
1
(
x
,
y
)
)
2
+
(
A
2
‚ąí
B
2
(
x
,
y
)
)
2
]
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
x
+
3
)
2
+
(
y
+
1
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=\left[1+\left(A_{1}-B_{1}\left(x,y\right)\right)^{2}+\left(A_{2}-B_{2}\left(x,y\right)\right)^{2}\right]\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=\left(x+3\right)^{2}+\left(y+1\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
where
=
{
A
1
=
0.5
sin
‚Ā°
(
1
)
‚ąí
2
cos
‚Ā°
(
1
)
+
sin
‚Ā°
(
2
)
‚ąí
1.5
cos
‚Ā°
(
2
)
A
2
=
1.5
sin
‚Ā°
(
1
)
‚ąí
cos
‚Ā°
(
1
)
+
2
sin
‚Ā°
(
2
)
‚ąí
0.5
cos
‚Ā°
(
2
)
B
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.5
sin
‚Ā°
(
x
)
‚ąí
2
cos
‚Ā°
(
x
)
+
sin
‚Ā°
(
y
)
‚ąí
1.5
cos
‚Ā°
(
y
)
B
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
1.5
sin
‚Ā°
(
x
)
‚ąí
cos
‚Ā°
(
x
)
+
2
sin
‚Ā°
(
y
)
‚ąí
0.5
cos
‚Ā°
(
y
)
{\displaystyle {\text{where}}={\begin{cases}A_{1}&=0.5\sin \left(1\right)-2\cos \left(1\right)+\sin \left(2\right)-1.5\cos \left(2\right)\\A_{2}&=1.5\sin \left(1\right)-\cos \left(1\right)+2\sin \left(2\right)-0.5\cos \left(2\right)\\B_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=0.5\sin \left(x\right)-2\cos \left(x\right)+\sin \left(y\right)-1.5\cos \left(y\right)\\B_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=1.5\sin \left(x\right)-\cos \left(x\right)+2\sin \left(y\right)-0.5\cos \left(y\right)\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
ŌÄ
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
ŌÄ
{\displaystyle -\pi \leq x,y\leq \pi }
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ó–ł—Ā—ā–Ķ—Ä–į-–Ē—Ć–Ķ–Ī–į-–Ę–Ķ—Ä–ł N. 1
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
1
+
9
29
‚ąĎ
i
=
2
30
x
i
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
‚ąí
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=x_{1}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1+{\frac {9}{29}}\sum _{i=2}^{30}x_{i}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)&=1-{\sqrt {\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}}\\\end{cases}}}
0
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{i}\leq 1}
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
30
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 30}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ó–ł—Ā—ā–Ķ—Ä–į-–Ē—Ć–Ķ–Ī–į-–Ę–Ķ—Ä–ł N. 2
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
1
+
9
29
‚ąĎ
i
=
2
30
x
i
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
‚ąí
(
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=x_{1}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1+{\frac {9}{29}}\sum _{i=2}^{30}x_{i}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)&=1-\left({\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
0
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{i}\leq 1}
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
30
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 30}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ó–ł—Ā—ā–Ķ—Ä–į-–Ē—Ć–Ķ–Ī–į-–Ę–Ķ—Ä–łn N. 3
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
1
+
9
29
‚ąĎ
i
=
2
30
x
i
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
‚ąí
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
‚ąí
(
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
)
sin
‚Ā°
(
10
ŌÄ
f
1
(
x
)
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=x_{1}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1+{\frac {9}{29}}\sum _{i=2}^{30}x_{i}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)&=1-{\sqrt {\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}}-\left({\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}\right)\sin \left(10\pi f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\end{cases}}}
0
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{i}\leq 1}
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
30
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 30}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ó–ł—Ā—ā–Ķ—Ä–į-–Ē—Ć–Ķ–Ī–į-–Ę–Ķ—Ä–łN. 4
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
91
+
‚ąĎ
i
=
2
10
(
x
i
2
‚ąí
10
cos
‚Ā°
(
4
ŌÄ
x
i
)
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
‚ąí
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=x_{1}\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=91+\sum _{i=2}^{10}\left(x_{i}^{2}-10\cos \left(4\pi x_{i}\right)\right)\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)&=1-{\sqrt {\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}}\end{cases}}}
0
‚ȧ
x
1
‚ȧ
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{1}\leq 1}
‚ąí
5
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle -5\leq x_{i}\leq 5}
2
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle 2\leq i\leq 10}
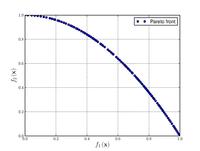
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ó–ł—Ā—ā–Ķ—Ä–į-–Ē—Ć–Ķ–Ī–į-–Ę–Ķ—Ä–ł N. 6
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
1
‚ąí
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
4
x
1
)
sin
6
‚Ā°
(
6
ŌÄ
x
1
)
f
2
(
x
)
=
g
(
x
)
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
g
(
x
)
=
1
+
9
[
‚ąĎ
i
=
2
10
x
i
9
]
0.25
h
(
f
1
(
x
)
,
g
(
x
)
)
=
1
‚ąí
(
f
1
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
)
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1-\exp \left(-4x_{1}\right)\sin ^{6}\left(6\pi x_{1}\right)\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1+9\left[{\frac {\sum _{i=2}^{10}x_{i}}{9}}\right]^{0.25}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)&=1-\left({\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
0
‚ȧ
x
i
‚ȧ
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{i}\leq 1}
1
‚ȧ
i
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle 1\leq i\leq 10}
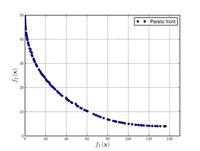
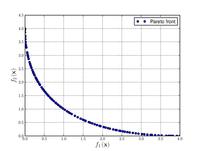
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –í–ł–Ĺ–Ĺ–Ķ—ā–į
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
0.5
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
+
sin
‚Ā°
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
3
x
‚ąí
2
y
+
4
)
2
8
+
(
x
‚ąí
y
+
1
)
2
27
+
15
f
3
(
x
,
y
)
=
1
x
2
+
y
2
+
1
‚ąí
1.1
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
(
x
2
+
y
2
)
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=0.5\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)+\sin \left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)&={\frac {\left(3x-2y+4\right)^{2}}{8}}+{\frac {\left(x-y+1\right)^{2}}{27}}+15\\f_{3}\left(x,y\right)&={\frac {1}{x^{2}+y^{2}+1}}-1.1\exp \left(-\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right)\\\end{cases}}}
‚ąí
3
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
3
{\displaystyle -3\leq x,y\leq 3}
–§—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł—Ź –ě—Ā—č–∑–ļ–ł –ł –ö—É–Ĺ–ī—É
F
1
(
x
)
=
‚ąí
25
(
x
1
‚ąí
2
)
2
‚ąí
(
x
2
‚ąí
2
)
2
{\displaystyle F_{1}(x)=-25\left(x_{1}-2\right)^{2}-\left(x_{2}-2\right)^{2}}
‚ąí
(
x
3
‚ąí
1
)
2
‚ąí
(
x
4
‚ąí
4
)
2
‚ąí
(
x
5
‚ąí
1
)
2
{\displaystyle -\left(x_{3}-1\right)^{2}-\left(x_{4}-4\right)^{2}-\left(x_{5}-1\right)^{2}}
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
)
=
F
1
(
x
)
f
2
(
x
)
=
‚ąĎ
i
=
1
6
x
i
2
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=F_{1}(x)\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=\sum _{i=1}^{6}x_{i}^{2}\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
‚ąí
2
‚Č•
0
g
2
(
x
)
=
6
‚ąí
x
1
‚ąí
x
2
‚Č•
0
g
3
(
x
)
=
2
‚ąí
x
2
+
x
1
‚Č•
0
g
4
(
x
)
=
2
‚ąí
x
1
+
3
x
2
‚Č•
0
g
5
(
x
)
=
4
‚ąí
(
x
3
‚ąí
3
)
2
‚ąí
x
4
‚Č•
0
g
6
(
x
)
=
(
x
5
‚ąí
3
)
2
+
x
6
‚ąí
4
‚Č•
0
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=x_{1}+x_{2}-2\geq 0\\g_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=6-x_{1}-x_{2}\geq 0\\g_{3}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=2-x_{2}+x_{1}\geq 0\\g_{4}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=2-x_{1}+3x_{2}\geq 0\\g_{5}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=4-\left(x_{3}-3\right)^{2}-x_{4}\geq 0\\g_{6}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=\left(x_{5}-3\right)^{2}+x_{6}-4\geq 0\end{cases}}}
0
‚ȧ
x
1
,
x
2
,
x
6
‚ȧ
10
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{1},x_{2},x_{6}\leq 10}
1
‚ȧ
x
3
,
x
5
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle 1\leq x_{3},x_{5}\leq 5}
0
‚ȧ
x
4
‚ȧ
6
{\displaystyle 0\leq x_{4}\leq 6}
CTP1 function (2 variables)
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
1
+
y
)
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
x
1
+
y
)
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=x\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=\left(1+y\right)\exp \left(-{\frac {x}{1+y}}\right)\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
0.858
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
0.541
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
)
‚Č•
1
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
0.728
exp
‚Ā°
(
‚ąí
0.295
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
)
‚Č•
1
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)&={\frac {f_{2}\left(x,y\right)}{0.858\exp \left(-0.541f_{1}\left(x,y\right)\right)}}\geq 1\\g_{1}\left(x,y\right)&={\frac {f_{2}\left(x,y\right)}{0.728\exp \left(-0.295f_{1}\left(x,y\right)\right)}}\geq 1\end{cases}}}
0
‚ȧ
x
,
y
‚ȧ
1
{\displaystyle 0\leq x,y\leq 1}
–ü—Ä–ĺ–Ī–Ľ–Ķ–ľ–į –ö–ĺ–Ĺ—Ā—ā—Ä-–≠–ļ—Ā–į
Minimize
=
{
f
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
x
f
2
(
x
,
y
)
=
1
+
y
x
{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=x\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)&={\frac {1+y}{x}}\\\end{cases}}}
s.t.
=
{
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
y
+
9
x
‚Č•
6
g
1
(
x
,
y
)
=
‚ąí
y
+
9
x
‚Č•
1
{\displaystyle {\text{s.t.}}={\begin{cases}g_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=y+9x\geq 6\\g_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=-y+9x\geq 1\\\end{cases}}}
0.1
‚ȧ
x
‚ȧ
1
{\displaystyle 0.1\leq x\leq 1}
0
‚ȧ
y
‚ȧ
5
{\displaystyle 0\leq y\leq 5}
–ü–į–Ĺ—ā–Ķ–Ľ–Ķ–Ķ–≤ –ź. –í., –ú–Ķ—ā–Ľ–ł—Ü–ļ–į—Ź –Ē. –í., –ē.–ź. –ź–Ľ–Ķ—ą–ł–Ĺ–į –ú–Ķ—ā–ĺ–ī—č –≥–Ľ–ĺ–Ī–į–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ–ĺ–Ļ –ĺ–Ņ—ā–ł–ľ–ł–∑–į—Ü–ł–ł. –ú–Ķ—ā–į—ć–≤—Ä–ł—Ā—ā–ł—á–Ķ—Ā–ļ–ł–Ķ —Ā—ā—Ä–į—ā–Ķ–≥–ł–ł –ł –į–Ľ–≥–ĺ—Ä–ł—ā–ľ—č // –ú.: –í—É–∑–ĺ–≤—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –ļ–Ĺ–ł–≥–į. 2013. 244 —Ā. ISBN 978-5-9502-0743-3
–°–Ķ—Ä–≥–ł–Ķ–Ĺ–ļ–ĺ –ź. –Ď. –Ę–Ķ—Ā—ā–ĺ–≤—č–Ķ —Ą—É–Ĺ–ļ—Ü–ł–ł –ī–Ľ—Ź –≥–Ľ–ĺ–Ī–į–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ–ĺ–Ļ –ĺ–Ņ—ā–ł–ľ–ł–∑–į—Ü–ł–ł.
‚ÜĎ Simionescu, P.A. (September 29 - October 2, 2002). New Concepts in Graphic Visualization of Objective Functions (PDF) . ASME 2002 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. Montreal, Canada. pp. 891‚Äď 897. –ź—Ä—Ö–ł–≤–ł—Ä–ĺ–≤–į–Ĺ–ĺ (PDF) 8 —Ź–Ĺ–≤–į—Ä—Ź 2017. –Ē–į—ā–į –ĺ–Ī—Ä–į—Č–Ķ–Ĺ–ł—Ź: 7 —Ź–Ĺ–≤–į—Ä—Ź 2017 . {{cite conference }}: –í–ł–ļ–ł–Ņ–Ķ–ī–ł—Ź:–ě–Ī—Ā–Ľ—É–∂–ł–≤–į–Ĺ–ł–Ķ CS1 (—Ą–ĺ—Ä–ľ–į—ā –ī–į—ā—č) (—Ā—Ā—č–Ľ–ļ–į )‚ÜĎ Solve a Constrained Nonlinear Problem - MATLAB & Simulink (–Ĺ–Ķ–ĺ–Ņ—Ä.) . www.mathworks.com . –Ē–į—ā–į –ĺ–Ī—Ä–į—Č–Ķ–Ĺ–ł—Ź: 29 –į–≤–≥—É—Ā—ā–į 2017. –ź—Ä—Ö–ł–≤–ł—Ä–ĺ–≤–į–Ĺ–ĺ 29 –į–≤–≥—É—Ā—ā–į 2017 –≥–ĺ–ī–į.‚ÜĎ Bird Problem (Constrained) | Phoenix Integration (–Ĺ–Ķ–ĺ–Ņ—Ä.) . –Ē–į—ā–į –ĺ–Ī—Ä–į—Č–Ķ–Ĺ–ł—Ź: 29 –į–≤–≥—É—Ā—ā–į 2017. –ź—Ä—Ö–ł–≤–ł—Ä–ĺ–≤–į–Ĺ–ĺ –ł–∑ –ĺ—Ä–ł–≥–ł–Ĺ–į–Ľ–į 29 –ī–Ķ–ļ–į–Ī—Ä—Ź 2016 –≥–ĺ–ī–į.‚ÜĎ Mishra, Sudhanshu. Some new test functions for global optimization and performance of repulsive particle swarm method (–į–Ĺ–≥–Ľ.) // MPRA Paper : journal. ‚ÄĒ 2006. –ź—Ä—Ö–ł–≤–ł—Ä–ĺ–≤–į–Ĺ–ĺ 4 –Ĺ–ĺ—Ź–Ī—Ä—Ź 2018 –≥–ĺ–ī–į.‚ÜĎ Townsend, Alex. Constrained optimization in Chebfun (–Ĺ–Ķ–ĺ–Ņ—Ä.) . chebfun.org (—Ź–Ĺ–≤–į—Ä—Ć 2014). –Ē–į—ā–į –ĺ–Ī—Ä–į—Č–Ķ–Ĺ–ł—Ź: 29 –į–≤–≥—É—Ā—ā–į 2017. –ź—Ä—Ö–ł–≤–ł—Ä–ĺ–≤–į–Ĺ–ĺ 29 –į–≤–≥—É—Ā—ā–į 2017 –≥–ĺ–ī–į.‚ÜĎ Simionescu, P.A. Computer Aided Graphing and Simulation Tools for AutoCAD Users (–į–Ĺ–≥–Ľ.) . ‚ÄĒ 1st. ‚ÄĒ Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press , 2014. ‚ÄĒ ISBN 978-1-4822-5290-3 .

![{\displaystyle f(\mathbf {x} )=An+\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left[x_{i}^{2}-A\cos(2\pi x_{i})\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1aa1c38ee739ca9cf4582867d74d469df4676cbc)




![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-20\exp \left[-0.2{\sqrt {0.5\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7f00d1325d65d088f8ae6a96137e62021107921d)
![{\displaystyle -\exp \left[0.5\left(\cos(2\pi x)+\cos(2\pi y)\right)\right]+e+20}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b3e3218e6b55ed49fe4627475644e5423fcd2af1)







![{\displaystyle f({\boldsymbol {x}})=\sum _{i=1}^{n-1}\left[100\left(x_{i+1}-x_{i}^{2}\right)^{2}+\left(x_{i}-1\right)^{2}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5ac655db50e19ee2f79a97196565e8773cd7d659)






![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\left[1+\left(x+y+1\right)^{2}\left(19-14x+3x^{2}-14y+6xy+3y^{2}\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2d020ed324ff07759faf17591157771b0e2cdf07)
![{\displaystyle \left[30+\left(2x-3y\right)^{2}\left(18-32x+12x^{2}+48y-36xy+27y^{2}\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/32e562da4f3219f9d66e059441c59e1d299e8557)
























![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-0.0001\left[\left|\sin x\sin y\exp \left(\left|100-{\frac {\sqrt {x^{2}+y^{2}}}{\pi }}\right|\right)\right|+1\right]^{0.1}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d591ae9bcf2feae162cd00398d78bb6870c82946)













![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.5+{\frac {\sin ^{2}\left(x^{2}-y^{2}\right)-0.5}{\left[1+0.001\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right]^{2}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/995008c6f10a14b44dac568cc544efb7d5ddd631)

![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=0.5+{\frac {\cos ^{2}\left[\sin \left(\left|x^{2}-y^{2}\right|\right)\right]-0.5}{\left[1+0.001\left(x^{2}+y^{2}\right)\right]^{2}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2458c352c0c0524648d8ef713bcea4e80df32fd8)















![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=\sin(y)e^{\left[(1-\cos x)^{2}\right]}+\cos(x)e^{\left[(1-\sin y)^{2}\right]}+(x-y)^{2}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7987d4a794d861e7ccd0795265841d3ca172cfae)





![{\displaystyle f(x,y)=-[\cos((x-0.1)y)]^{2}-x\sin(3x+y)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8dac25f97d0b720512d72c313000d5fb5c7d033a)
![{\displaystyle x^{2}+y^{2}<\left[2\cos t-{\frac {1}{2}}\cos 2t-{\frac {1}{4}}\cos 3t-{\frac {1}{8}}\cos 4t\right]^{2}+[2\sin t]^{2}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/57168b192e685c6144e3a9527b12087ac7cb11b4)





![{\displaystyle x^{2}+y^{2}\leq \left[r_{T}+r_{S}\cos \left(n\arctan {\frac {x}{y}}\right)\right]^{2}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1fc42adcc2095ed0c0214a74799db7ee2fac9923)



















![{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=\sum _{i=1}^{2}\left[-10\exp \left(-0.2{\sqrt {x_{i}^{2}+x_{i+1}^{2}}}\right)\right]\\&\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=\sum _{i=1}^{3}\left[\left|x_{i}\right|^{0.8}+5\sin \left(x_{i}^{3}\right)\right]\\\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a545df8c08a178973284eae8924aab67ce46077a)










![{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left(x,y\right)&=\left[1+\left(A_{1}-B_{1}\left(x,y\right)\right)^{2}+\left(A_{2}-B_{2}\left(x,y\right)\right)^{2}\right]\\f_{2}\left(x,y\right)&=\left(x+3\right)^{2}+\left(y+1\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e6b4a1275cbe615b285fbbcdb840a9a488360cc5)














![{\displaystyle {\text{Minimize}}={\begin{cases}f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1-\exp \left(-4x_{1}\right)\sin ^{6}\left(6\pi x_{1}\right)\\f_{2}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)\\g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)&=1+9\left[{\frac {\sum _{i=2}^{10}x_{i}}{9}}\right]^{0.25}\\h\left(f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right),g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)\right)&=1-\left({\frac {f_{1}\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}{g\left({\boldsymbol {x}}\right)}}\right)^{2}\\\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/73a519e6f7ca429b41031cd0873fce161941b009)