Public-key cryptography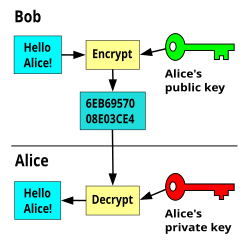 Public-key cryptography, also called asymmetric cryptography, is a communication where people send messages that can only be read by those who have the key. A MetaphorThis kind of cryptography is like two magical paper shredders. Each can shred messages that only the other can unshred. ExplanationIn public key cryptography, each user has a pair of cryptographic keys, which are long strings of random data. One of the keys is public, and can be shared with anyone, even bad actors. One of the keys is private, and must be kept secret. Information encrypted with the public key can be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa. Incoming messages are encrypted with the recipient's public key and can only be decrypted with their corresponding private key. The keys are related mathematically, but it is nearly impossible to get a private key from a public key. The two main branches of public key cryptography are:
They are often used together on the same message. Related pages
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia













