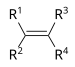
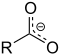
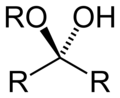
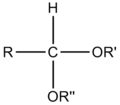
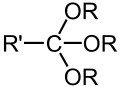
ਕਿਰਿਆਸ਼ੀਲ ਸਮੂਹ ਕਾਰਬਨੀ ਰਸਾਇਣ ਵਿਗਿਆਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਿਰਤੀਮੂਲਕ ਸਮੂਹ (ਹੋਰ ਨਾਂ ਕਿਰਿਆਸ਼ੀਲ ਸਮੂਹ ਅਤੇ ਕਿਰਿਆਤਮਕ ਸਮੂਹ ਹਨ) ਅਣੂਆਂ ਵਿਚਲੇ ਪਰਮਾਣੂਆਂ ਜਾਂ ਜੋੜਾਂ ਦੇ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਝੁੰਡਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਹੜੇ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਅਣੂਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਰਸਾਇਣਕ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਭਾਵ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਿਰਤੀ ਲਈ ਜੁੰਮੇਵਾਰ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ। ਕੋਈ ਇੱਕ ਕਿਰਿਆਸ਼ੀਲ ਸਮੂਹ ਇੱਕੋ ਹੀ ਜਾਂ ਇੱਕੋ ਜਿਹੀ ਰਸਾਇਣਕ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਲੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਭਾਵੇਂ ਜਿਸ ਅਣੂ ਦਾ ਉਹ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਹੈ, ਦਾ ਅਕਾਰ ਕਿੰਨਾ ਵੀ ਹੋਵੇ।[1][2] ਪਰ ਉਹਦੀ ਤੁਲਨਾਤਮਕ ਕਿਰਿਆਸ਼ੀਲਤਾ ਨੇੜਲੇ ਹੋਰ ਬਿਰਤੀਮੂਲਕ ਸਮੂਹ ਬਦਲ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ। ਆਮ ਬਿਰਤੀਮੂਲਕ ਸਮੂਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਾਰਨੀਹੇਠਾਂ ਆਮ ਬਿਰਤੀਮੂਲਕ ਸਮੂਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਸੂਚੀ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਹੈ। ਫ਼ਾਰਮੂਲਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ R ਅਤੇ R' ਚਿੰਨ, ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ਉੱਤੇ, ਨਾਲ਼ ਲੱਗੀ ਹਾਈਡਰੋਜਨ ਜਾਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਲੰਬਾਈ ਵਾਲੀ ਹਾਈਡਰੋਕਾਰਬਨ ਦੀ ਪਾਸੇ ਵਾਲੀ ਲੜੀ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕ ਹਨ ਪਰ ਕਈ ਵਾਰ ਪਰਮਾਣੂਆਂ ਦੇ ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਝੁੰਡ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਸਾ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ। ਹਾਈਡਰੋਕਾਰਬਨ
There are also a large number of branched or ring alkanes that have specific names, e.g., tert-butyl, bornyl, cyclohexyl, etc. Hydrocarbons may form charged structures: positively charged carbocations or negative carbanions. Carbocations are often named -um. Examples are tropylium and triphenylmethyl cations and the cyclopentadienyl anion. ਹੈਲੋਜਨਾਂ ਵਾਲ਼ੇ ਸਮੂਹHaloalkanes are a class of molecule that is defined by a carbon–halogen bond. This bond can be relatively weak (in the case of an iodoalkane) or quite stable (as in the case of a fluoroalkane). In general, with the exception of fluorinated compounds, haloalkanes readily undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions or elimination reactions. The substitution on the carbon, the acidity of an adjacent proton, the solvent conditions, etc. all can influence the outcome of the reactivity.
ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਵਾਲ਼ੇ ਸਮੂਹCompounds that contain C-O bonds each possess differing reactivity based upon the location and hybridization of the C-O bond, owing to the electron-withdrawing effect of sp-hybridized oxygen (carbonyl groups) and the donating effects of sp2-hybridized oxygen (alcohol groups).
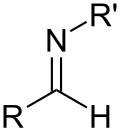
ਨਾਈਟਰੋਜਨ ਵਾਲ਼ੇ ਸਮੂਹCompounds that contain nitrogen in this category may contain C-O bonds, such as in the case of amides.
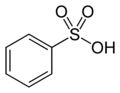
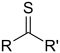
ਗੰਧਕ ਵਾਲ਼ੇ ਸਮੂਹCompounds that contain sulfur exhibit unique chemistry due to their ability to form more bonds than oxygen, their lighter analogue on the periodic table. Substitutive nomenclature (marked as prefix in table) is preferred over functional class nomenclature (marked as suffix in table) for sulfides, disulfides, sulfoxides and sulfones.
ਫ਼ਾਸਫ਼ੋਰਸ ਵਾਲ਼ੇ ਸਮੂਹCompounds that contain phosphorus exhibit unique chemistry due to their ability to form more bonds than nitrogen, their lighter analogues on the periodic table.
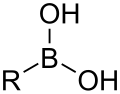
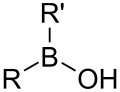
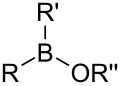
ਬੋਰਾਨ ਵਾਲ਼ੇ ਸਮੂਹCompounds containing boron exhibit unique chemistry due to their having partially filled octets and therefore acting as Lewis acids.
ਬਾਹਰੀ ਕੜੀਆਂ
ਹਵਾਲੇ
|
Portal di Ensiklopedia Dunia